10-3
7
10
7
7
7
7
7
7
10.1 Overview
(2) Writable/readable devices
(a) Writable/readable device names
The following table shows the devices that can be written to/read from the Univesal
model QCPU in another CPU with the multiple CPU high-speed transmission dedicated
instruction.
:Settable :Settable with conditions
SB, SW, SM, and SD include system information area. Take care not to destroy
the system information when writing data to the devices above with the
D(P).DDWR instruction of the multiple CPU high-speed transmission dedicated
instruction.
(3) Specification method of a device and writable/readable device range
There are two methods for specifying a device in another CPU: device specification and
string specification. They differ in writable/readable device range to another CPU.
(a) Device specification
The device specification is a method to directly specify a device in another CPU to be
written/read.
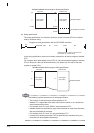
Program for device specification with the DP.DDWR instruction
In the device specification, data can be written/read within the device range of host CPU.
For example, when data register in host CPU is 12k points and data register in another CPU
is 16k points, data can be written/read by 12k points from the start of the data register in
another CPU.
Category Type Device name
Setting of target
device
Remarks
Internal user device
Bit device
X, Y, M, L, B, F, SB
Requirements for the setting
• Digits are specified by 16 bits (4 digits).
• The start bit device is multiples of
16(10H).
Word device
T, ST, C, D, W, SW ––
Internal system device
Bit device
SM
Requirements for the setting
• Digits are specified by 16 bits (4 digits).
• The start bit device is multiples of
16(10H).
Word device
SD ––
File register Word device
R, ZR ––
X0
DP.DDWR H3E1 D0 D100 D200 M0
Directly specifies "D200", a
device in another CPU to be
written.