Charger Handbook
Version: Chg1.4
Energizer Battery Manufacturing Inc. | 800-383-7323 (USA-CAN) | www.energizer.com
©2008 Energizer – Contents herein does not constitute a warranty of service, features or performance Page 3 of 4
NiMH Battery Chargers
Handbook and Application Manual
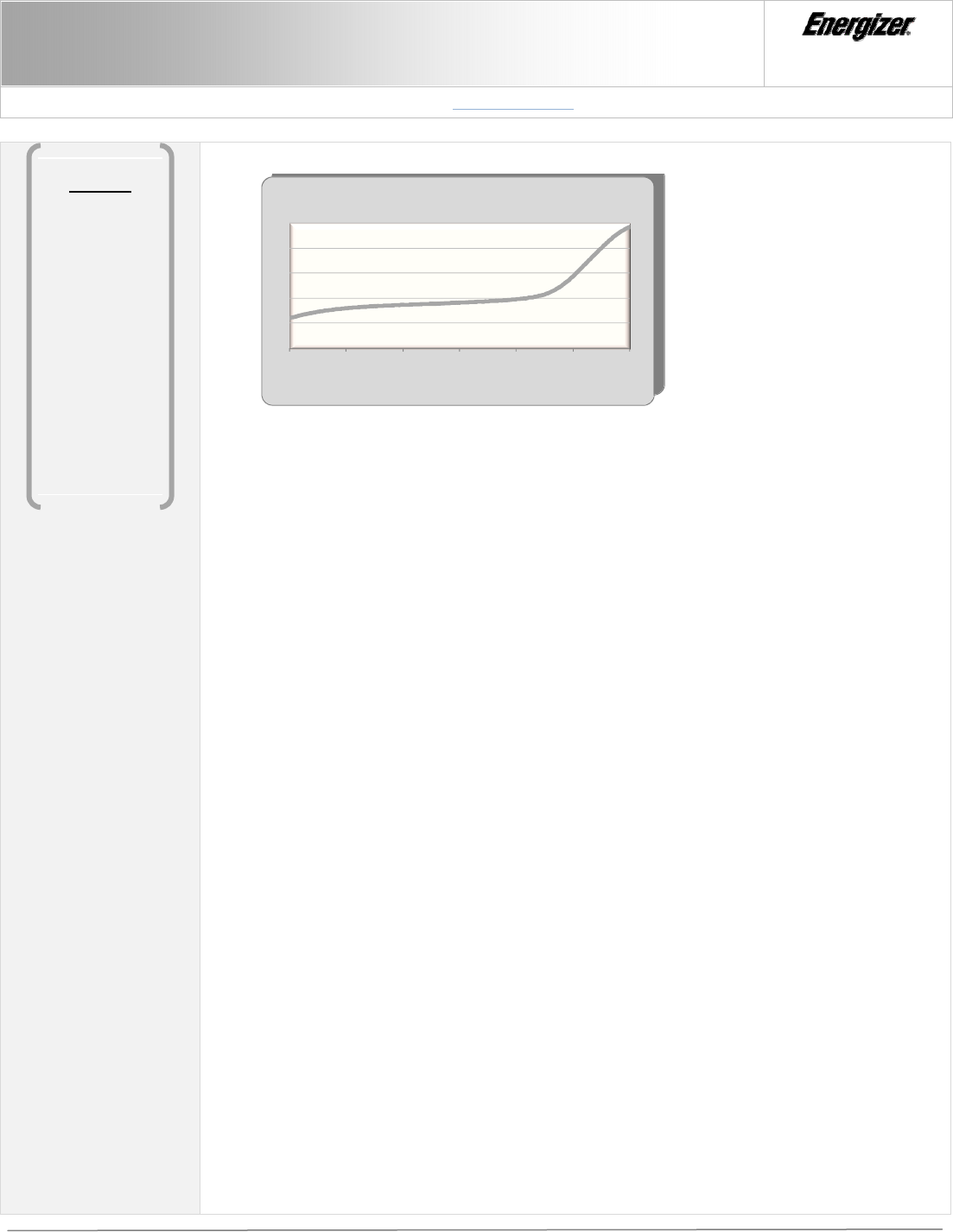
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 120%
Temperature
% Charge
Temperature During Charging
NiMH Battery
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 120%
Temperature
% Charge
Temperature During Charging
NiMH Battery
(fig. 2) Charging Temperature
Timer Control:
A maximum charge time is set as a backup to avoid overcharging.
Cost to Charge Batteries (electricity)
The typical cost to charge a set of batteries will be less than one cent per charge. For example, the
Energizer
® CHDC7 charger has an input rating of 7 Watts. In 6.5 hours of charge, it would require (6.5
hours X 7 Watts) 46 Watt hours or .046 kWh. If the cost of electricity is 10 cents per kWh, a charge
would cost (.046 kWh X 10 cents) ~1/2 cent.
Chargers that have an Energy Star rating are designed to consume minimal power when plugged in but
not charging.
Summary
The
Energizer
® family of chargers offers a wide range of features to fulfill the specific needs of
customers. However, there are often tradeoffs between some of these features concerning, price,
charge time and optimal battery performance. Typically optimum battery performance will be achieved
by using a relatively slow charge rate.
Glossary
C Rate:
The current (in Amps or mA) required to charge a battery in 1 hour up to its full rated capacity. For
example, 2.45 A for a 2450 mAh battery.
Capacity:
A measure of how much charge a battery can hold. This is typically stated in Amp-Hours or mAh.
Cell Reversal:
Reversing polarity of terminals of a cell or battery due to over-discharge.
Charge, State of (SOC):
Condition in terms of the rated capacity remaining at a given point in time. The SOC is typically stated
as a percentage.
Charging:
Process of supplying electrical energy for conversion to stored chemical energy.
Contents
Introduction
General
Information
Charge Control
“Smart” Charger
Control Techniques
Cost to Charge
(electricity)
Summary
Glossary






