4 5
1. Hold tools by insulated gripping sur-
faces when performing an operation
where the cutting tool may contact
hidden wiring or its own cord. Contact
with a "live" wire will make exposed
metal parts of the tool "live" and shock
the operator.
2. Wear ear protectors with impact
drills. Exposure to noise can cause
hearing loss.
3. Use auxiliary handles supplied with
the tool. Loss of control can cause
personal injury.
4. Keep hands away from all cutting
edges and moving parts.
5. Maintain labels and nameplates.
These carry important information.
If unreadable or missing, contact a
MILWAUKEE service facility for a free
replacement.
POWER TOOL USE AND CARE
16. Do not force the power tool. Use the
correct power tool for your applica-
tion. The correct power tool will do the
job better and safer at the rate for which
it was designed.
17. Do not use the power tool if the switch
does not turn it on and off. Any power tool
that cannot be controlled with the switch is
dangerous and must be repaired.
18. Disconnect the plug from the power
source and/or the battery pack from
the power tool before making any
adjustments, changing accessories,
or storing power tools. Such preven-
tive safety measures reduce the risk of
starting the power tool accidentally.
19. Store idle power tools out of the
reach of children and do not allow
persons unfamiliar with the power
tool or these instructions to operate
the power tool. Power tools are danger-
ous in the hands of untrained users.
20. Maintain power tools. Check for
misalignment or binding of moving
parts, breakage of parts and any
other condition that may affect the
power tool's operation. If damaged,
have the power tool repaired before
use. Many accidents are caused by
poorly maintained power tools.
21. Keep cutting tools sharp and clean.
Properly maintained cutting tools with
sharp cutting edges are less likely to
bind and are easier to control.
22. Use the power tool, accessories and
tool bits etc., in accordance with
these instructions and in the manner
intended for the particular type of
power tool, taking into account the
working conditions and the work to
be performed. Use of the power tool for
operations different from those intended
could result in a hazardous situation.
SERVICE
28. Have your power tool serviced by a
qualifi ed repair person using only
identical replacement parts. This will
ensure that the safety of the power tool
is maintained.
23. Ensure the switch is in the off posi-
tion before inserting battery pack.
Inserting the battery pack into power
tools that have the switch on invites
accidents.
24. Recharge only with the charger speci-
fi ed by the manufacturer. A charger
that is suitable for one type of battery
pack may create a risk of fi re when used
with another battery pack.
BATTERY TOOL USE AND CARE
SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES
25. Use power tools only with specifi cally
designated battery packs. Use of any
other battery packs may create a risk of
injury and fi re.
26. When battery pack is not in use, keep
it away from other metal objects like
paper clips, coins, keys, nails, screws,
or other small metal objects that can
make a connection from one terminal
to another. Shorting the battery terminals
together may cause burns or a fi re.
27. Under abusive conditions, liquid may
be ejected from the battery, avoid
contact. If contact accidentally oc-
curs, fl ush with water. If liquid con-
tacts eyes, additionally seek medical
help. Liquid ejected from the battery
may cause irritation or burns.
3
2
8
9
1
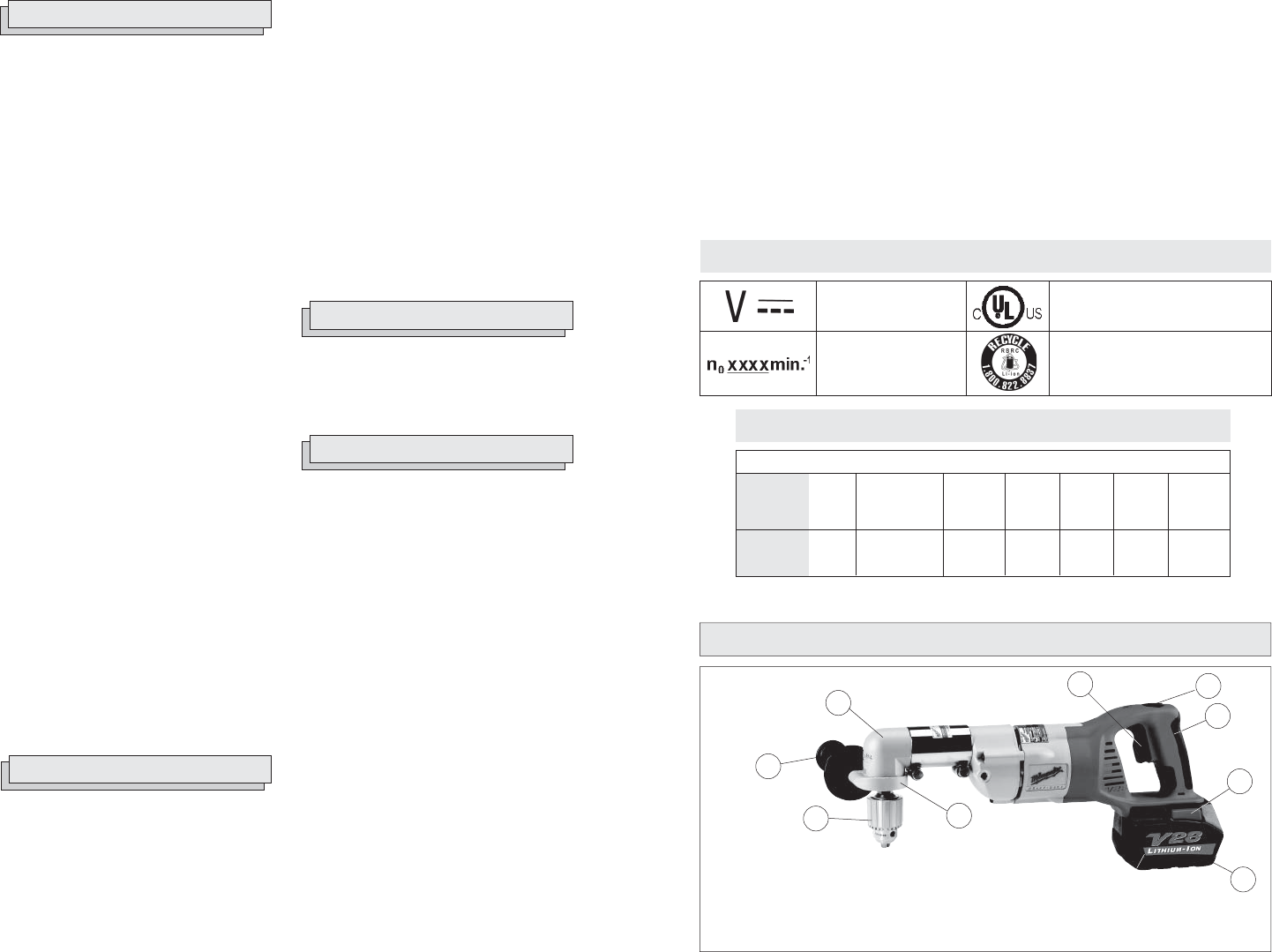
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
6
4
5
7
1. Handle
2. Forward/Reverse/Trigger lock switch
3. Trigger
4. Right angle drive unit
5. Side handle
Symbology
Volts Direct
Current
No Load Revolutions
per Minute (RPM)
Underwriters Laboratories, Inc.,
United States and Canada
Properly Recycle
Lithium-Ion Batteries
RAD
No load
RPM
Hi 0 - 1000
Lo 0 - 400
Volts
DC
28
Flat
Boring
Bits
1-1/2"
1-1/2"
Cat. No.
0721-20
Auger
Bit
3/4"
1-1/2"
Selfeed
Bit
1"
2-9/16"
Hole
Saw
3-1/2"
4-1/2"
Ship
Auger
Bit
1"
1-1/2"
Wood
Specifi cations
6. WARNING: Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other
construction activities contains chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Some examples of these chemicals are:
• lead from lead-based paint
• crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry products, and
• arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work.
To reduce your exposure to these chemicals: work in a well ventilated area, and work
with approved safety equipment, such as those dust masks that are specially designed
to fi lter out microscopic particles.
6. Chuck
7. Ring clamp
8. Battery pack
9. Battery pack release buttons


















