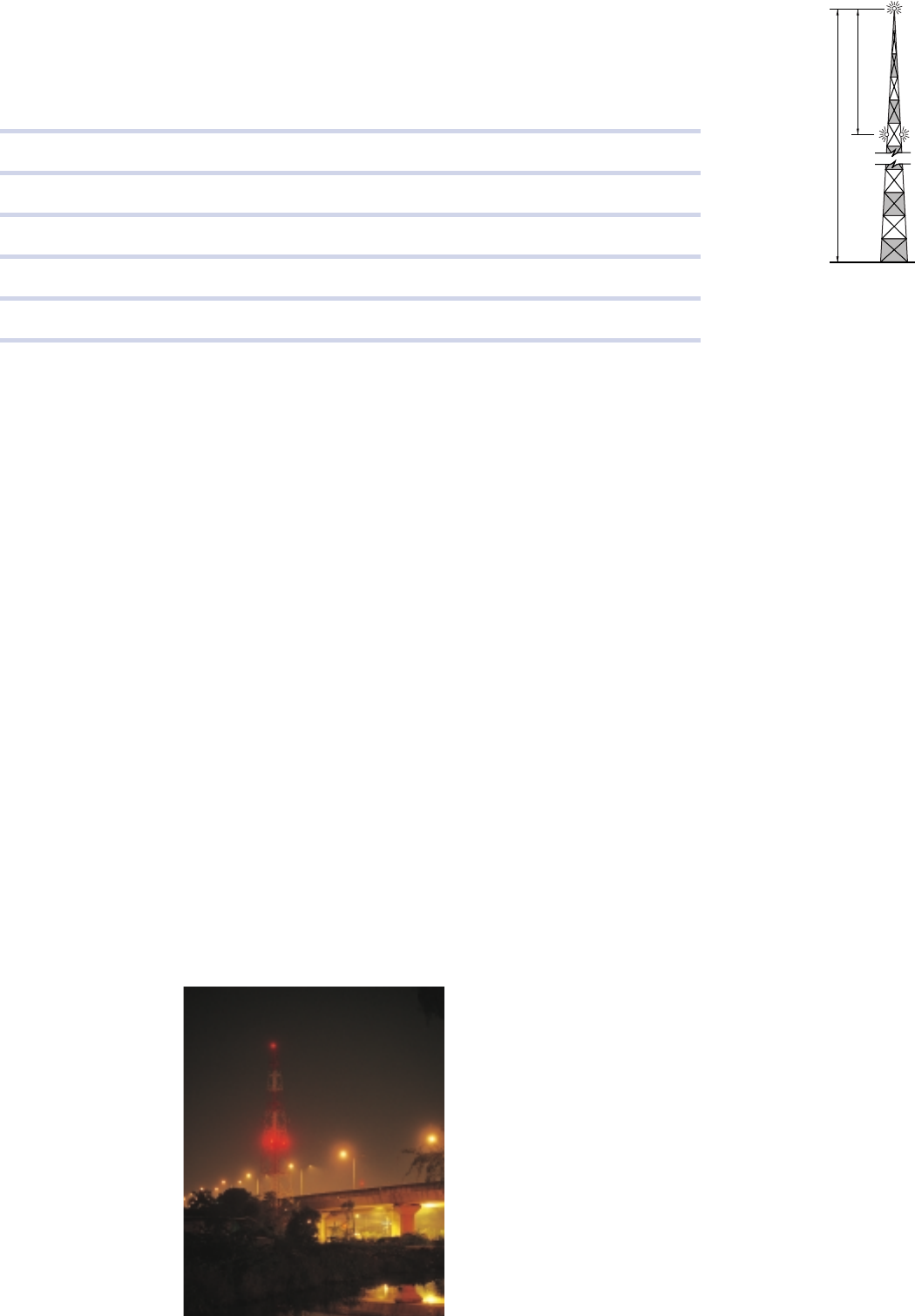
Y
X
N1
N2
Traditionally obstacle light has used incandescent
technology. The short lifetime of the incandescent
lamps of approximately 1,000 hours and their
susceptibility to failure caused by vibration required
that the fitting have two lamps. This ensured that in
the event of one failure the other lamp could take
over. This system required constant and frequent
lamp changing, costly maintenance, and was high in
energy consumption.
Now, the benefits of the latest in Light Emitting
Diode
(LED) technology can provide a far superior
solution. By taking advantage of its long lifetime of
approximately 100,000 hours, low power consump-
tion, and resistance to shock and vibration of
LEDs,
the Philips ObstiVision provides an ideal, mainte-
nance free solution to obstruction lighting system.
The standards and requirements of obstacle light
Obstruction lighting systems must meet the
requirements of the
ICAO International Civil
Aviation Organisation Standards and Recommended
Practices: Aerodromes- Annex 14- Volume 1, 3rd
Edition, July 1999, Chapter 6.
The key points that must be adhered to are
• To reduce the hazards to the aircraft, obstacles
above the horizontal surface should be lighted to
indicate the presence of the obstacles
• The light must be fixed, and red in colour
• Minimum peak intensity at background
luminance of up to 500cd/m2: 10cd for low
intensity type A and 32cd for low intensity type B
• Vertical beam spread of not less than 10 degrees
• Minimum intensity (cd) at given elevation
angles when the light is levelled: +6 degrees:
10cd for low intensity type A and 32cd for low
intensity type B
• Minimum intensity (cd) at given elevation angles
when the light is levelled: +10 degrees: 10cd for
low intensity type A and 32cd for low
intensity type B
• In addition to specified values, lights shall have
sufficient intensity to ensure conspicuity at
elevation angles between +/
-
0 degrees and
50 degrees
ObstiVision in practice
ObstiVision is a dedicated maintenance-free
obstacle light for aviation warning purposes. Light
emitting diode
(LED) technology is chosen to be
the light source of this product. ObstiVision is
suitable to be used as a Low Intensity, Type A and
Type B obstacle lights according to
ICAO standard.
Typical applications for Obstivison would include
telecommunication towers, tall buildings, airport
areas and power transmission towers.
The guidelines for the type and location of
obstacle lights are contained within the
ICAO
standard as described.
Location of obstacle lights
Number of lights = N =
—————
Y (metres)
45
Light spacing = X =
——– ≤ 45 m
Y
N
obstruction lighting system
the new generation
Obstacle light to mark the presence of tall structures that may
present hazards to air navigation at night time is a legal
requirement. The lighting system must be designed to meet
International Civil Aviation Organisation
(ICAO) standards for
product specification and placement.








