• 12 •
IMPORTANT: Using the ENGINE START feature WITHOUT a battery
installed in the vehicle could cause damage to the vehicle’s electrical
system.
If the engine does turn over, but never starts, there is not a problem with
the starting system; there is a problem somewhere else with the vehicle.
STOP cranking the engine until the other problem has been diagnosed
and corrected.
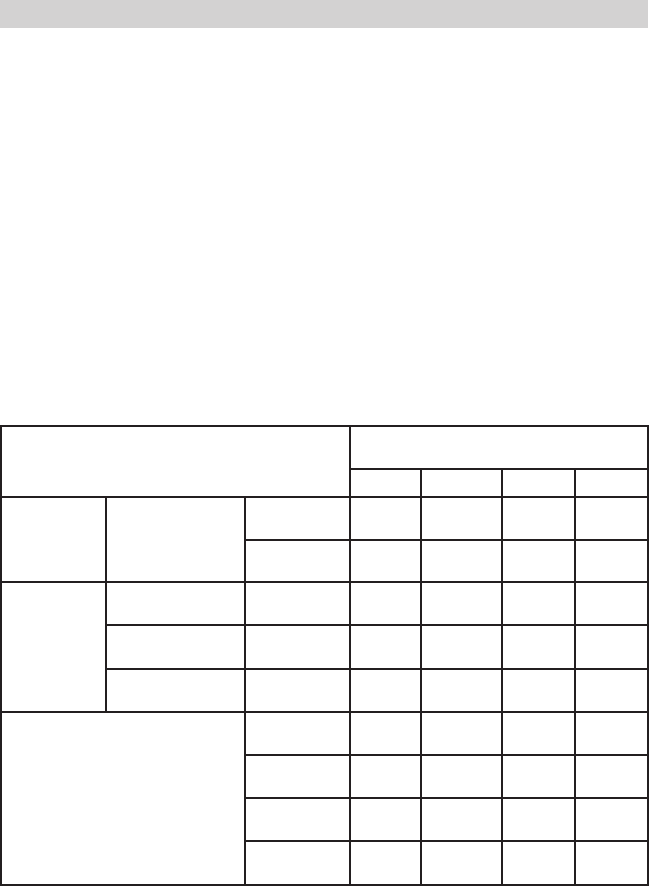
CALCULATING CHARGE TIME13.
The Chart Method13.1
Use the following table to more accurately determine the time it will take to
bring a battery to full charge. First, identify where your battery ts into the
chart.
Small batteries – motorcycle, garden tractors, etc. – are usually rated in •
Ampere Hours (AH). For example: 6, 12, 32 AH etc.
Batteries in cars and smaller trucks are usually rated in Reserve Capacity •
(RC), Cold-Cranking Amps (CCA), or both.
Marine or deep-cycle batteries are usually rated in Reserve Capacity •
(RC).
NR means that the charger setting is NOT RECOMMENDED.•
Find your batteries rating on the chart below and note the charge time
given for each charger setting. The times given are for batteries with a
50-percent charge prior to recharging. Add more time for severely dis-
charged batteries.
BATTERY SIZE/RATING
CHARGE RATE/
CHARGING TIME - HOURS
4 AMP 20 AMP 40 AMP 70 AMP
SMALL
BATTERIES
Motorcycle, gar-
den, tractor, etc.
6 - 12 AH 2 - 4 NR NR NR
12 - 32 AH 4 - 10 NR NR NR
CAR/
TRUCKS
200 - 315 CCA 40 - 60 RC 11 - 14
60 - 90
min.
30 - 40
min.
20 - 30
min.
315 - 550 CCA 60 - 85 RC 14 - 18
90 - 120
min.
45 min -
1 hr
30 - 40
min.
550 - 1000 CCA 85 - 190 RC 18 - 35
2 - 3.5
hrs.
1 - 2 hr
45 - 60
min.
MARINE/DEEP CYCLE
80 RC 18 105 min. 1 hr NR
140 RC 27
2 hrs., 45
min.
1 hr and
15 min
NR
160 RC 30 3 hrs. 1.5 hrs NR
180 RC 33 3.5 hrs. 2 hrs NR