9A
Non-Vehicular or Vehicular
Non-vehicular applications include stationary configurations as well as mobile configurations that are not integrated into a vehicle’s electrical
system. In a parallel connection, your Inverter/Charger’s Nominal DC Input Voltage (listed in the Specifications section must match the
voltage of your battery or batteries. For example, a 12V DC Inverter/Charger would require 12V DC from your battery system.
In a series connection, your Inverter/Charger’s Nominal DC Input Voltage must match the number of batteries multiplied by their voltage. For
example, a 12V DC Inverter/Charger would require two 6V batteries connected in series (12 = 2 × 6).
In vehicular applications, your Inverter/Charger’s Nominal DC Input Voltage must match the voltage of your battery or batteries—
12 Volts. Although it is possible to connect your Inverter/Charger to the main battery within your vehicle’s electrical system, in the normal
vehicular context, the Inverter/Charger is connected to one or more dedicated auxiliary (house) batteries which are isolated from the drive
system to prevent possible draining of the main battery.
Contact Tripp Lite technical support for assistance with additional parallel, series or series/parallel connections.
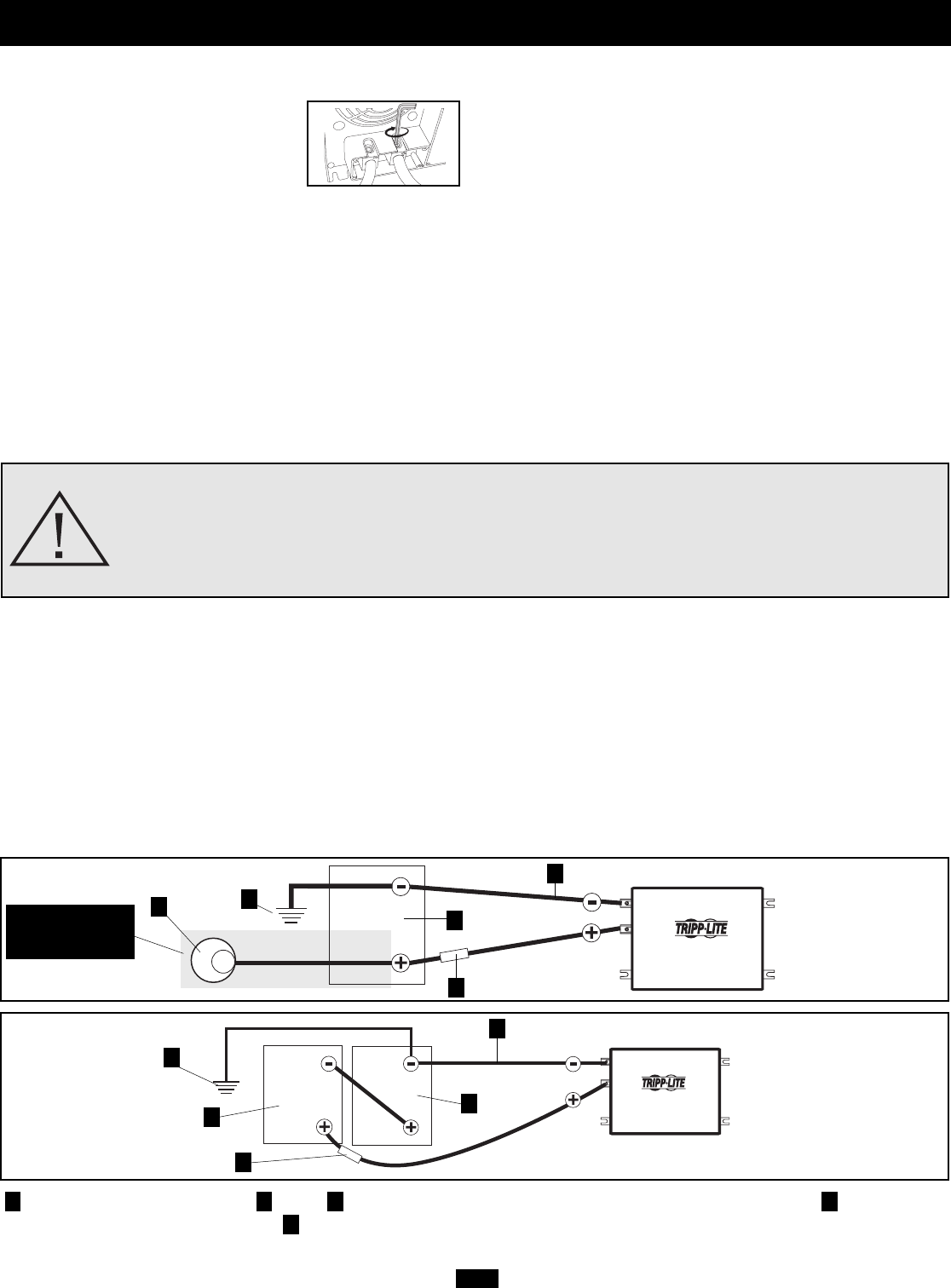
Earth or Vehicle/Boat Battery Ground Battery UL-Listed Fuse & Fuse Block [mounted within 45 cm (18 inches) of the battery] Large Diameter
Cabling, Maximum 2/0 Gauge to Fit Terminals Alternator (for vehicle or boat connection only)
5
4321
12 Volt Inverter/Charger
12 Volts
Single Battery Connection
4
1
2
3
12 Volt Inverter/Charger
6 Volts
6 Volts
Multiple Battery Connection (Series)
1
2
4
3
Battery Connection
5
Optional connection
for Vehicular
applications only.
• Connect DC Wiring: Though your
Inverter/Charger is a high-efficiency con-
verter of electricity, its rated output capacity
is limited by the length and gauge of the
cabling running from the battery to the unit.
Use the shortest length and largest diameter
cabling (maximum 2/0 gauge) to fit your Inverter/Charger’s DC Input
terminals. Shorter and heavier gauge cabling reduces DC voltage drop
and allows for maximum transfer of current. Your Inverter/Charger
is capable of delivering peak wattage at up to 200% of its rated con-
tinuous wattage output for brief periods of time. See Specifications
page for details. Heavier gauge cabling should be used when contin-
uously operating heavy draw equipment under these conditions.
Tighten your Inverter/Charger and battery terminals to approximate-
ly 3.5 Newton-meters of torque to create an efficient connection and
to prevent excessive heating at this connection. Insufficient tighten-
ing of the terminals could void your warranty. See Specifications
page for Minimum Recommended Cable Sizing Chart.
• Connect Ground: Using a #8 AWG wire or larger directly connect
the Main Ground Lug to the vehicle’s chassis or earth ground. See
the Feature Identification section to locate the Main Ground Lug on
your specific Inverter/Charger model. All installations must comply
with national and local codes and ordinances.
• Connect Fuse: NEC (National Electrical Code) article 551
requires that you connect all of your Inverter/Charger’s positive DC
Terminals directly to a UL-listed fuse(s) and fuse block(s) within 45
cm (18 inches) of the battery. The fuse’s rating must equal or exceed
the Minimum DC Fuse Rating listed in your Inverter/Charger’s
specifications. See Specifications for fuse and fuse block recom-
mendations. See diagrams below for proper fuse placement.
Connect your Inverter/Charger to your batteries using the following procedures:
WARNING!
• Failure to properly ground your Inverter/Charger to a vehicle’s chassis or earth ground may result
in a lethal electrical shock hazard.
• Never attempt to operate your Inverter/Charger by connecting it directly to output from an
alternator rather than a battery or battery bank.
• Observe proper polarity with all DC connections.
DC Connectors
2














