Architecture
59
6.2.5 Status register and Cache register mode bit and exception processing
When the R3900 Processor Core responds to an exception, it saves the values of the current operating
mode bit (KUc) and current interrupt enabled mode bit (IEc) in the previous mode bits (KUp and IEp).
It saves the values of the previous mode bits (KUp and IEp) in the old mode bits (KUo and IEo). The
current mode bits (KUc and IEc) are cleared to 0, with the processor going to kernel mode and
interrupts disabled.
Likewise, the R3900 Processor Core saves the values of the current data cache auto-lock mode bit
(DALc) and current instruction cache auto-lock mode bit (IALc) in the previous mode bits (DALp and
IALp). It saves the values of the previous mode bits (DALp and IALp) in the old mode bits (DALo
and IALo). The current mode bits (DALc and IALc) are cleared to 0, disabling the data cache and
instruction cache lock functions.
Provision of these three-level mode bits means that, before the software saves the Status register
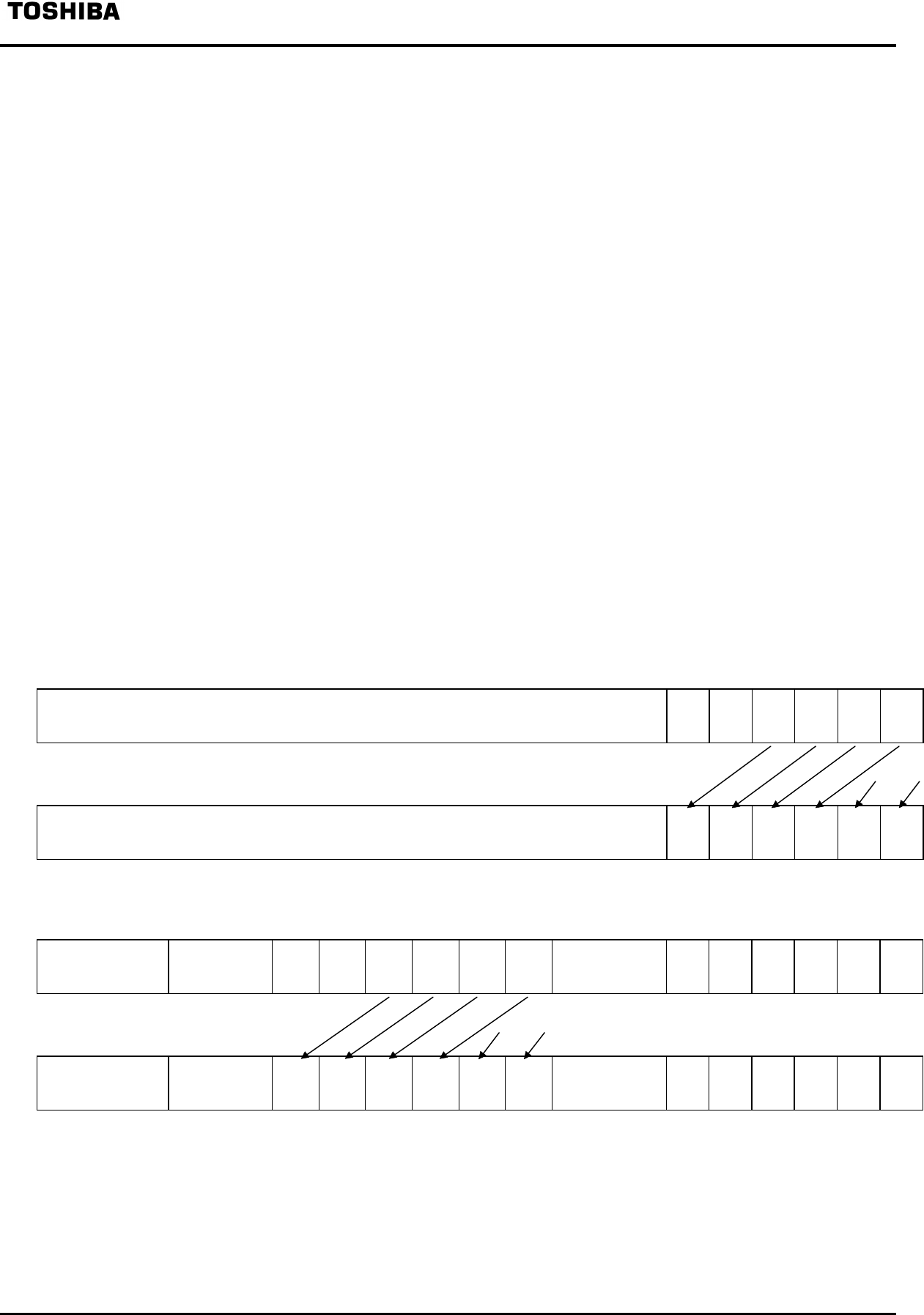
contents, the R3900 Processor Core can respond to two levels of exceptions. Figure 6-6 shows the
Status register and Cache register save operations used by the R3900 Processor Core in exception
processing.
KUo IEo KUp IEp KUc IEc
Exception raised
KUo IEo KUp IEp KUc IEc
(a) Status register
0 0 0 IAL
o
DAL
o
IAL
p
DAL
p
IAL
c
DAL
c
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Exception raised
0 0 0 IAL
o
DAL
o
IAL
p
DAL
p
IAL
c
DAL
c
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
(b) Cache register
Figure 6-6. Status regisuter and cache register when an exception is raised
0 0
0 0
