Output Connections and Operating Information
54
Open Sense Leads
The sense leads are part of the supply’s feedback path. Connect them in such a way so that they do not inadvertently
become open circuited. The power supply includes protection resistors that reduce the effect of open sense leads during
remote-sensing operation. If the sense leads open during operation, the supply returns to the local sensing mode, with the
voltage at the output terminals approximately equal to the programmed value.
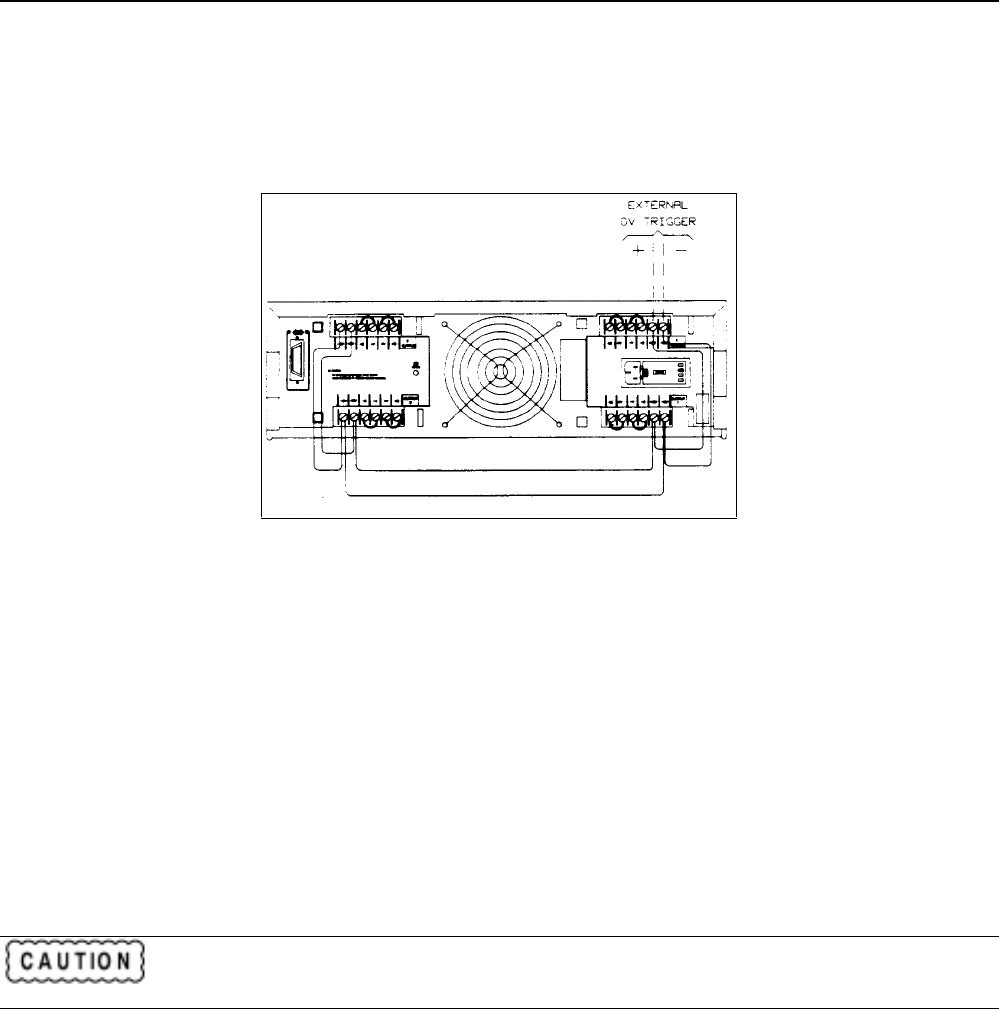
Overvoltage Trigger Connections
Each output of your power supply has two OV terminals on its rear panel terminal block. These terminals are labeled +OV
and -OV. By connecting the OV terminals all in parallel as shown in Figure 4-7, an overvoltage shutdown on any one
output will also trigger the overvoltage on the remaining outputs. Any number of OV terminals up to eight sets can be
strapped together. Observe polarity when connecting the OV terminals in parallel.
Figure 4-7 Overvoltage Connections
The overvoltage trip point for each output can be set either from the front panel or by remote programming. You can also
externally fire the overvoltage circuit of one or more outputs by applying a 5 volt pulse of at least 50
µ
s to any pair of OV
terminals (see Figure 4-8). As long as all OV terminals are wired together, the outputs will be crowbarred simultaneously .
External Trigger Circuit
Figure 4-8 illustrates a recommended external circuit that can be used to provide an OV trip signal to the OV terminals.
This circuit configuration provides good noise immunity and protects against the voltage pulse that is returned from the OV
terminals every time that the overvoltage circuit fires. It can be operated from a wide range of bias voltages provided the
input limiting resistors are chosen as tabulated in the figure. If it is not required to trip the OV with a TTL signal, then a
bias supply, switch, current limiting resistor (R2), and protection diode are all that are required. Note that with the unit off
(ac power removed), the + OV and - OV terminals are inactive.
The internal equivalent OV circuit is shown in Figure 4-9. Note the internal DC blocking capacitor, bleed resistor, and
noise bypass capacitors.
Do not exceed 50 volts maximum between the + OV and the - OV terminals. The OV terminals are
rated at ±240 Vdc (including external OV voltage) from chassis ground or any other output terminals.