Output Connections and Operating Information
58
CC Operation
For CC operation, set the output voltages as outlined in CV operation (page 57), or alternatively, program the voltage
settings of both outputs to the same voltage limit point. Then program the current of each output so that the sum of both
currents equals the total desired operating current. The simplest way to accomplish this is to program each output to one
half of the total desired operating current. Both outputs will operate in the CC mode.
Remote Sensing
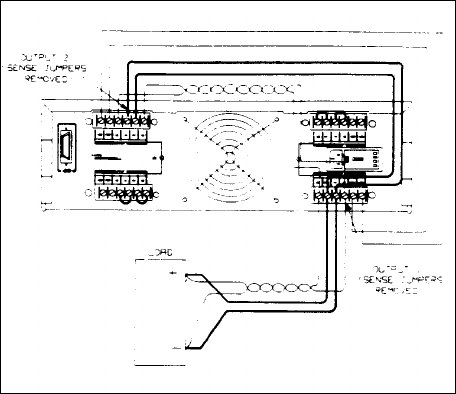
If it is necessary to remote voltage sense at the load, parallel the sense leads of output 1 with the sense leads of output 2 and
connect to the load as shown in Figure 4-12. The outputs can be programmed as previously described.
Figure 4-12. Parallel Connections with Remote Sensing
Specifications for Parallel Operation
Specifications for outputs operating in parallel can be obtained from the specifications for single outputs. Most
specifications are expressed as a constant or as a percentage (or ppm) plus a constant. For parallel operation, the percentage
portion remains unchanged while constant portions or any constants are changed as indicated below.
Current All parallel specifications referring to current are twice the single output
specification except for programming resolution which is the same for both
single output and parallel output operation.
Voltage All parallel specifications referring to voltage are the same as for a single
output except for CV load effect, CV load cross regulation, CV source effect,
and CV short term drift. Below 4 V on 25 W outputs and 2 V on 50 W
outputs, these are all twice the voltage programming accuracy (including the
percentage portion). CV load effect above 4 V on 25 W outputs and 2 V on
50 W outputs, could be twice the load effect specification for a single output.
CV output noise for output voltages less than 4 V on 25 W outputs, and 2 V
on 50 W outputs, may be slightly higher than the output noise for a single
output.
Load Transient Recovery
Time
350 µs maximum to recover within 100 mV of nominal value following a load change
within the range of 0 to full load.