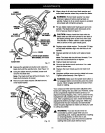
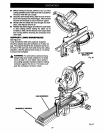
C-CLAMP Fig. 28
mm Loosen the bevel lock knob and move the saw
arm to the left to the desired bevel angle.
• Bevel angles can be sat from 0° to 45°.
mm For your convenience there is a double scale
located on the mounting bracket. See Fig'ure27. If
one side becomes difficultto read as you move
the saw arm to the left, simply refer to the other
side. Align the indicator point for the side you
choose with the desired angle.
• Once the saw arm has been set at the desired
angle, securely tighten the bevel lock knob.
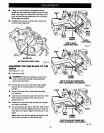
• Place the workpiece fiat on the miter table with
one edge securely against the fence. If the board
is warped, place the convex side against the
fence. If the concave edge of a board is placed
against the fence, the board could collapse on the
blade at the end of the cut, jamming the blade.
See Figures 33 and 34.
• When cutting long pieces of lumber or molding,
support the opposite end of the stock with a roller
stand or with a work surface level with the saw
table.
J Align the cutting line on the workpiece with the
edge of saw blade.
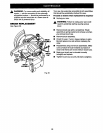
• Grasp the stock firmly with one hand and secure it
against the fence. Use the optional work clamp or
a C-clamp to secure the workpiece when pos-
sible. See Figure 28.
_._ WARNING: To avoid serious personal injury,
keep your hands outside the no hands zone; at
least 3 in. from blade. Never perform any cuffing
operation freehand (without holding workpiece
against the fence). The blade could grab the
workpiece if it slips or twists.
• Before turning on the saw, perform a dry run of
the cutting operation just to make sure that no
problems will occur when the cut is made.
• Grasp the saw handle firmly, slide the lock-off
lever back, then squeeze the switch trigger. Allow
several seconds for the blade to reach maximum
speed.
• Slowly lower the blade into and through the
workpiece. See Figure 28.
• Release the switch trigger and allow the saw
blade to stop rotating before raising the blade out
of workpiece. Wait until the electric brake stops
blade from turning before removing the workpiece
from miter table.
COMPOUND MITER CUT
A compound miter cut is a cut made using a miter
angle and a bevel angle at the same time, This type of
cut is used to make picture frames, cut molding, make
boxes with sloping sides, and for certain roof framing
cuts. H
To make this type of cut the control arm on the miter
table must be rotated to the correct angle and the saw
arm must be tilted to the correct bevel angle. Care
should always be taken when making compound miter
setups due to the interaction of the two angle settings.
Adjustments of miter and bevel settings are interde-
pendent with one another. Each time you adjust the
miter saffing you change the effect of the bevel
setting. Also, each time you adjust the bevel setting
you change the effect of the miter setting.
It may take several settings to obtain the desired cut.
The first angle setting should be checked after satting
the second angle, since adjusting the second angle
affects the first.
Once the two correct settings for a particular cut have
been obtained, always make a test cut in scrap
material before making a finish cut in good material.
21