12
Fig. 12
A
B
Fig. 13
C
D
E
B
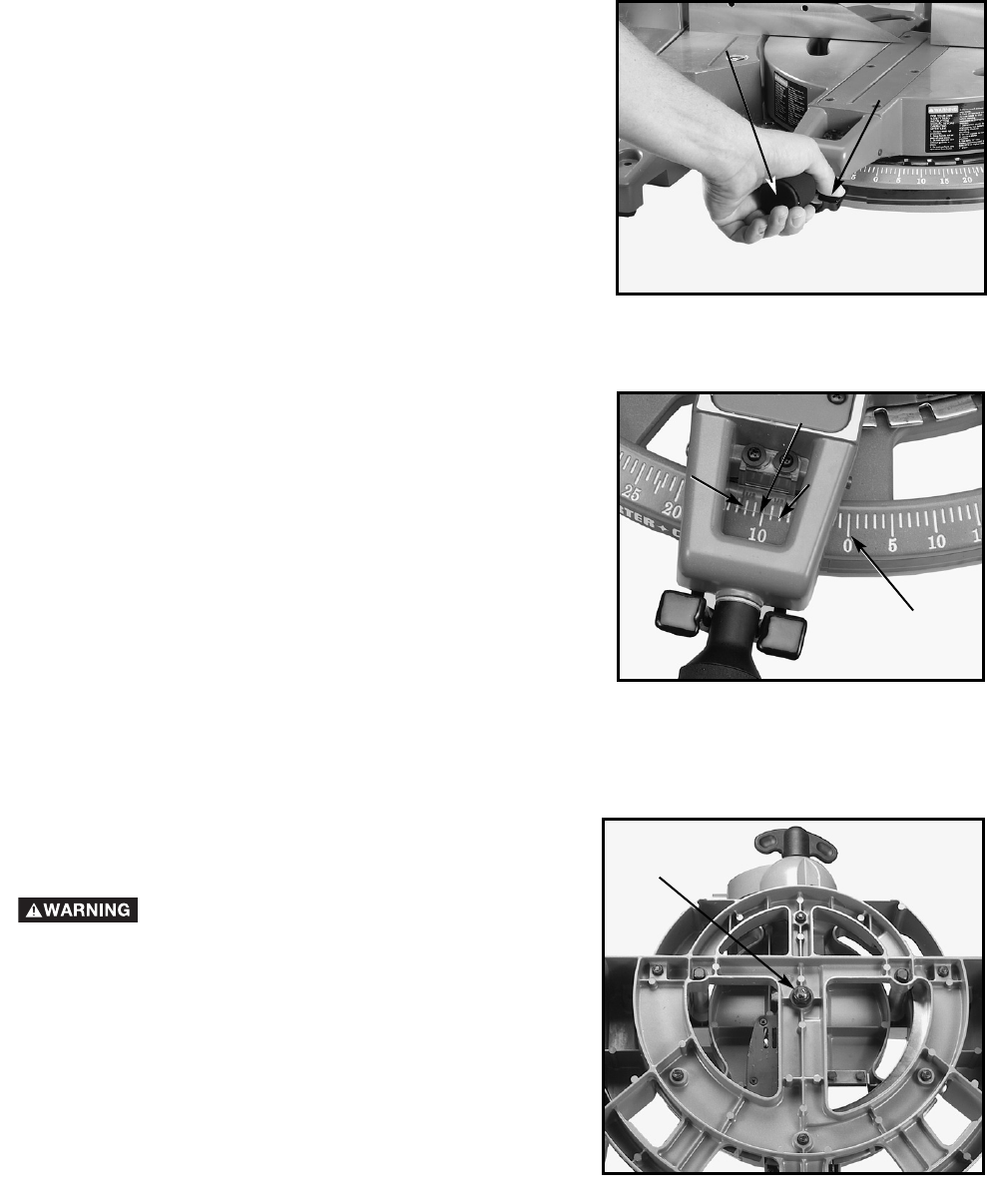
1. The compound miter saw will cut any angle from a
straight 0° cut to 47° right and left. Turn locking knob
(A) Fig. 12 counterclockwise, depress lock lever (B),
and rotate table to desired position.
2. The compound miter saw is equipped with positive
stops at the 0° cut-off position and at the 15°, 22.5°,
31.62°, and 45° left and right positions.
3. The center line, (C) Fig. 13, on the cursor indicates
the actual angle of cut. Each scale line (B) represents
1°. In effect, when the center line (C) is moved from
one line to the next on the scale, the angle of the cut
is changed by 1°.
4. The pointer is provided with two additional lines (D)
and (E), Fig. 13. This allows movement of the control
arm exactly 1/2°. For example, assume the center
line (C) is pointing to the 10° mark on the scale, as
indicated, and and the angle of cut is 1/2° to the
right. Move the control arm until the right line (E) lines
up with the next line on the scale. The angle of cut
will then be changed 1/2° to the right. If you change
the angle of cut 1/2° to the left, use the left line (D) in
the same manner.
ADJUSTING SLIDING FIT BETWEEN
MOVABLE TABLE AND BASE
1. DISCONNECT THE MACHINE FROM
THE POWER SOURCE.
2. To adjust the sliding fit between the movable table and
the base, turn nut (A) Fig. 14, clockwise to increase
the sliding fit (opposite to decrease the fit). This
adjustment should not be so tight that it restricts the
rotating movement of the table, or so loose that it
affects the accuracy of the saw.
Fig. 14
A
ROTATING THE TABLE
FOR MITER SAW CUTTING


















