If the size of the workpiece causes your hand to be inside the table hazard zone (see section “TABLE HAZARD
ZONE” SEE FIG. 21), use a clamp to secure the workpiece.
AUXILIARY WOOD FENCE
When performing multiple or repetitive cut-off operations
that result in small cut-off pieces (one inch or less), the saw
blade can catch the cut-off pieces and project them out of the machine or
into the blade guard and housing, possibly causing damage and/or injury. In
order to limit the possibility of personal injury or blade guard damage, mount
an auxiliary wood fence to your saw.
Holes are provided in the fence to attach an auxiliary fence (A) and (B) (Fig.
32B). This auxiliary fence is constructed of straight wood approximately
1/2” thick. Side A should be approximately 5.25" high by 10.5" long and
side B should be approximately 3" high by 10.5" long.
NOTE: The auxiliary fence (A) is used only with the saw blade in the 0° bevel
position (90°) to the table. The auxiliary fence must be removed for all bevel
cuts (blade tilted).
Fig. 34
Fig. 35
FENCE
FENCE
BLADE
BLADE
CORRECT
INCORRECT
CUTTING ALUMINUM
To reduce the risk of injury, use the proper blade when cutting this type of material.
Aluminum extrusions (aluminum screens and storm windows) can easily be cut with your miter saw. When cutting aluminum
extrusions, or other sections that can be cut with a saw blade and are within the capacity of the machine, position the material so
that the blade is cutting through the smallest cross-section, as shown in Fig. 34 The wrong way to cut aluminum angles is illustrated
in Fig. 35. Be sure to apply a stick wax (similar to Johnson’s stick wax #140) to the blade before cutting any aluminum stock. This
stick wax is available at most industrial mill supply houses. The stick wax provides proper lubrication and keeps chips from adhering
to the blade.
Never apply lubricant to the blade while the saw is running.
Make sure that the fence is clear of the guard and blade before operating the saw.
Fig. 32B
1. Before cutting, make certain that the cutting arm and table area are at their correct settings and firmly locked in place.
2. Before cutting, determine that the workpiece is the right size for the saw.
3. Place the workpiece on the table and hold or clamp it firmly against the fence.
4. For best results, cut at a slow, even cutting rate.
5. Never attempt freehand cutting (cutting a workpiece that is not held firmly against the fence and table).
12
TYPICAL OPERATIONS AND HELPFUL HINTS
B
A
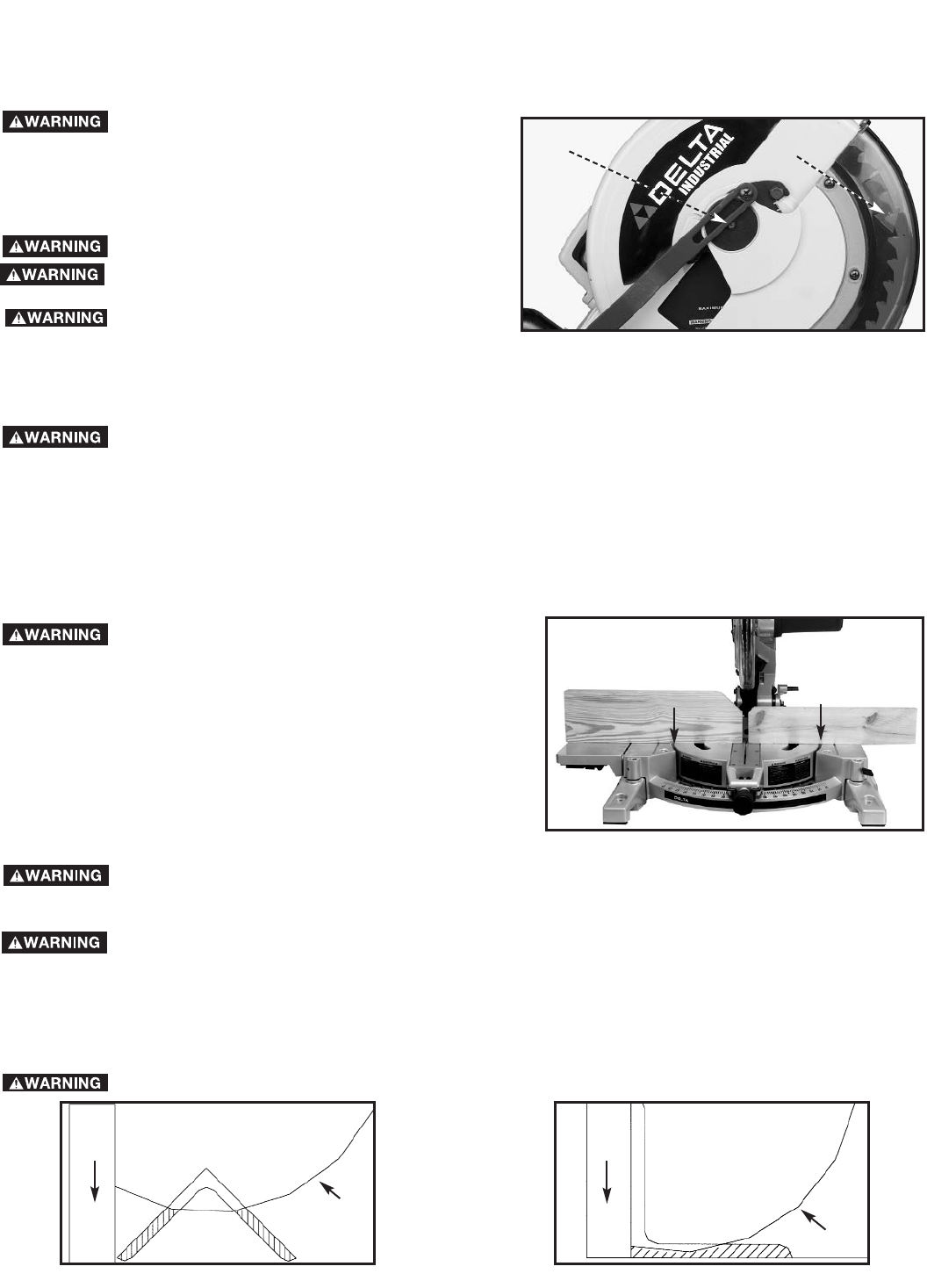
ADJUSTING LOWER BLADE GUARD
This machine incorporates a blade guard (A) Fig. 32A to cover the rear section of the blade. After an extended period of use, the
movable lower blade guard may not operate smoothly when the cuttinghead is lowered. This can be corrected by adjusting nut (B)
until the lower blade guard moves freely.
Overtightening the nut could impair guard
movement.
NOTE: This unit has been designed with an
articulating rear guard. Before contacting the
workpiece, the rear guard will rotate upward to
expose more of the blade as the cuttinghead is
lowered.
Do not remove any of the blade guards.
Make sure that all guards are in place and
functioning properly before operating the saw.
Make sure that the fences are clear of the guard
and blade before operating the saw.
Fig. 32A
B
A


















