-14-
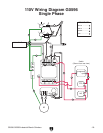
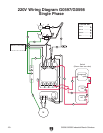
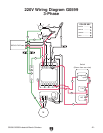
G0596-G0599 Industrial Bench Grinders
Wheel Care
Your safety when grinding depends, on a large
part, on the condition of the wheel during grind
-
ing. A wheel in poor condition presents the possi
-
bility of breaking apart during rotation and injuring
the operator and others in the area.
Here are some tips to help you avoid breaking
the wheel:
• Always transport, store and handle wheels
with care. Wheels may be damaged if they
are dropped or if heavy objects are stacked
on them.
• Select the right grinding wheel for the job.
DO NOT grind material inappropriate for the
wheel type.
• Select the right wheel for the machine. A
machine that rotates at a higher RPM than
the wheel is rated for may cause the wheel
to fly apart.
• Mount the wheels properly. (See the
Wheel
Replacement instructions on Page 16 for
guidance.)
• Do not abuse the wheel by jamming the work
into the grinding wheel with excessive force
that causes the grinder to bog down, or apply
pressure to stop the wheel after turning the
grinder OFF.
• Dress the wheel when necessary. Do not
allow it to become glazed.
• Always spin water/coolant out of the wheel
before turning the grinder
OFF. This may
take 5–10 minutes. (If moisture is left on the
wheel, the wheel may warp.)
• Do not store wheels in damp or wet loca
-
tions.
• Do not grind on the side of the wheel unless
wheel is designed for side grinding.
• Do not overtighten the nut when mounting
the wheel.
Wheel Selection
The Model G0596/G0597 only accepts Type 1
wheels with a 1" bore. The Model G0598/G0599
only accepts Type 1 wheels with a 1
1
⁄4" bore.
Aluminum oxide and silicon carbide wheels are
marked in a somewhat uniform manner by all the
major manufacturers. Understanding these mark
-
ings will help you understand the capabilities of
various wheels. Always refer to the manufactur
-
er’s grinding recommendations when selecting a
wheel for your project.
The basic format for wheel numbering is:
Prefix
Abrasive
Type
Grit Size Grade
Bond
Type
1 A 60 L V
The Prefix is the manufacturer’s designation for a
particular wheel type (eg, Type 1 wheels).
The most common Abrasive Types used are A
for Aluminum Oxide, C for Silicon Carbide, and
occasionally SG for Seeded Gel.
The Grit Size is a number that refers to the size
of the abrasive grain in the wheel. The lower the
number, the coarser the wheel. Ten is a very
coarse wheel for roughing and 220 is usually the
upper range for fine finish work.
Grade is an indication of the hardness of the
wheel—“A” being the softest and “Z” being the
hardest.
Bond Type refers to the type of bonding material
used to hold the abrasive material. Most general
purpose wheels will have a “V” indicating Vitrified
Clay is used. Vitrified Clay provides high strength
and good porosity. The other common bond type
is “B” for resin where synthetic resins are used.
These are used to grind cemented carbide and
ceramic materials.
Note:
There may be other numbers inserted that
have meaning for a particular type of wheel. Refer
to the manufacturer’s technical data for a com
-
plete explanation.