"')"
BdYZa<%,'%GB[\#H^cXZ&&$&%
Headstock Travel
(Z-Axis & Rotation)
Ndjgb^aa]VhVYdkZiV^aZYXdajbci]ViVaadlhndj
idgZedh^i^dci]Z]ZVYhidX`Vadc\i]ZO"Vm^hVcY
X]Vc\Zidda^c\l^i]djiadh^c\ndjgVa^\cbZcil^i]
V ]daZ dg b^aa^c\ eVi]#;dg Vc\aZY b^aa^c\ deZgV"
i^dch!i]Z]ZVYhidX`XVcWZgdiViZYaZ[iVcYg^\]i
)*#
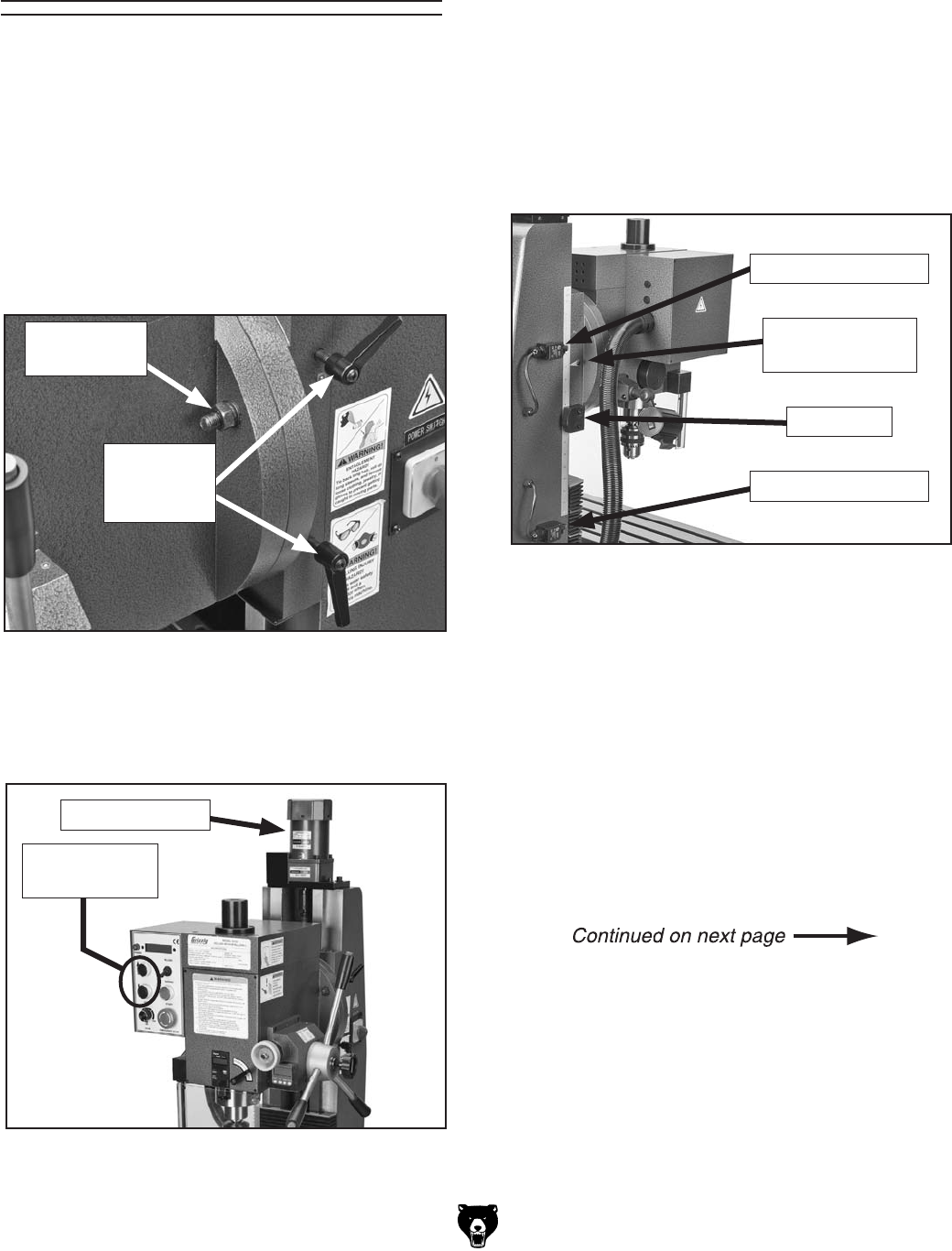
Raising & Lowering
1. JcadX`i]Z]ZVYhidX`ha^YZadX`aZkZgh]dlc
^cFigure 18#
3. DWhZgkZ i]Z ]Z^\]i hXVaZ dc i]Z aZ[i h^YZ
Xdajbch]dlc^cFigure 20 idYZiZgb^cZi]Z
]ZVYhidX`igVkZa#I]^hhXVaZ^hWgd`ZcYdlc
^c
&
¿-\gVYjVi^dch#
Note: When the headstock reaches a point
of travel where the leadscrew has run out of
thread, a stop block (see Figure 20) contacts
either the upper or lower limit switch to stop
the elevation motor from over running the
physical limitations of the leadscrew length,
which would cause damage.
AdlZgA^b^iHl^iX]
JeeZgA^b^iHl^iX]
Hide7adX`
:aZkVi^dcHXVaZ
VcYEd^ciZg
Figure 20. 8dajbchl^iX]ZhVcYhXVaZ#
Note: For maximum spindle rigidity when
milling, keep the spindle retracted into the
headstock as far as possible with the quill
lock lever locked and with the fine feed lock
knob tightened.
2. Dci]ZXdcigdaeVcZaejh]i]ZJEdg9DLC
WjiidchhZZFigure 19idgV^hZdgadlZgi]Z
]ZVYhidX`l^i]i]ZZaZkVi^dcbdidg#
Figure 19. O"Vm^hXdcigda#
Figure 18. =ZVYhidX`ha^YZXdcigdah#
JeVcY9dlc
7jiidch
:aZkVi^dcBdidg
=ZVYhidX`
Ha^YZAdX`
AZkZg
=ZVYhidX`
I^ai=ZmCji


















