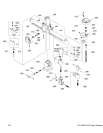
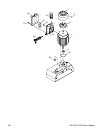
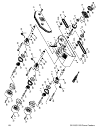
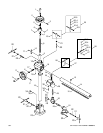
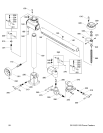
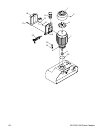
-36- G1128/G1129 Power Feeders
CORRECTIVE ACTION
1. Check power line for proper voltage.
2. Inspect all lead connections on motor for
loose or open connections.
1. Inspect cord or plug for damaged insulation
and shorted wires.
2. Inspect all connections on motor for loose
or shorted terminals or worn insulation.
3. Install correct fuses or circuit breakers.
1. Reduce load on power line.
2. Increase wire sizes or reduce length of wire.
3. Request a power check from the power
company.
1. Reduce load on motor.
2. Clean out motor to provide normal air circu-
lation.
1. Inspect connections on motor for loose or
shorted terminals or worn insulation.
2. Correct the low voltage conditions.
3. Install correct fuses or circuit breakers.
4. Reduce load on motor.
Feed workpiece slower.
1. Clean and wax the tabletop on a regular
basis. Do not use silicone lubricants.
2. Wipe sawdust from boards and wheels.
Sand wheels slightly if they become glazed.
TROUBLESHOOTING
SYMPTOM
Motor will not start.
Motor will not start; fuses
or circuit breakers blow.
Motor fails to develop full
power (power output of
motor decreases rapidly
with decrease in voltage
at motor terminals).
Motor overheats.
Motor stalls (resulting in
blown fuses or tripped cir-
cuit breaker).
Machine slows when
operating.
Workpiece stalls, but
wheels continue to turn.
POSSIBLE CAUSE
1. Low voltage.
2. Open circuit in motor
or loose connections.
1. Short circuit in line
cord or plug.
2. Short circuit in motor
or loose connections.
3. Incorrect fuses or cir-
cuit breakers in power
line.
1. Power line overloaded
with lights, appliances,
and other motors.
2. Undersized wires or
circuits too long.
3. General overloading of
power company facili-
ties.
1. Motor overloaded.
2. Air circulation through
the motor restricted.
1. Short circuit in motor
or loose connections.
2. Low voltage.
3. Incorrect fuses or cir-
cuit breakers in power
line.
4. Motor overloaded.
Applying too much
pressure to workpiece.
1. Excessive friction
between workpiece
and table.
2. Insufficient friction
between the rollers
and workpiece.