Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
The MIB is a virtual mapping of variables to physical hardware and its related devices. SNMP
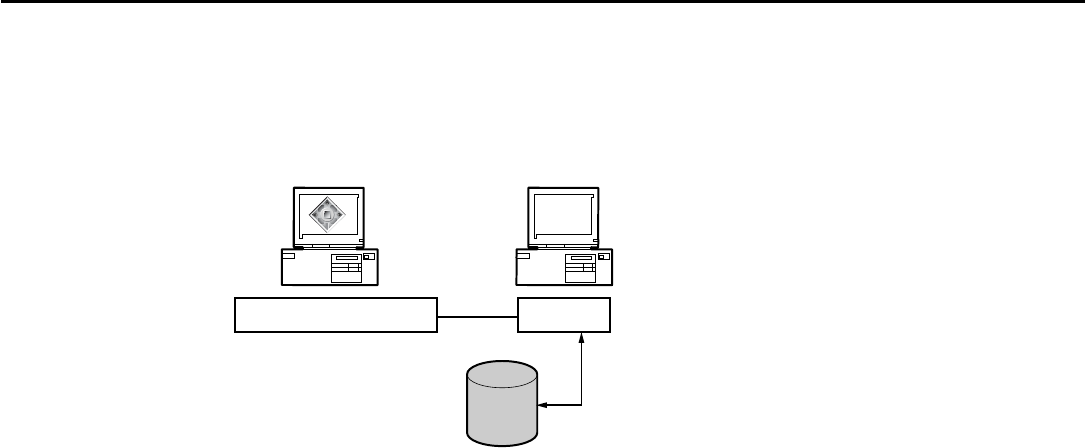
abstracts the control of the device through these variables. The below figure illustrates the
interaction of the management application, the agents on a device, and the MIB databases. The
configuration in this diagram shows two MIB databases. Multiple MIB databases within the
same configuration should have the same versions of a MIB. MIB databases must be
synchronized so interpretations of data are uniform.
The MIB is analogous to a database schema because it represents data and data structures.
MIBs have been defined for TCP/IP routers and hosts, interface types, such as token ring and
FDDI, and devices, such as servers and bridges. HP has defined MIBs for all of its SNMP-
capable devices. These MIBs are pre-compiled into the database and can be used by Insight
Manager 7.
Other third-party devices like routers and hubs exist on a network. Vendors of these network
devices also define MIBs. When the vendor MIB is registered into the database, you can use
Insight Manager 7 to monitor and control the devices.
The MIB structure is explained in the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) Standards RFC 1155.
Because the MIB structure resembles the directory and subdirectory file structure used for an
operating system, it is often referred to as a tree with a root.
MIB files often contain groups of variables that define the types of information that can be
retrieved from a device. MIB information and characteristics include an object identifier, or OID,
and a unique identifier that identifies the MIB and the variable. A variable can have one or
more values. The OID is in numeric dot format. The tree structure determines the unique name
and OID notation for each manageable entity.
MIB variables declare certain characteristics of the device, such as the operating system. HP
MIBs include information like version numbers and product names. For example, the following
table shows variables for an HP server running Windows NT 4.0. The values for the variables
include the product and other information derived from the MIB database.
Management Application Agents
MIBs
3


















