4
5
Grounded Tools: Tools with Three Prong Plugs
Tools marked “Grounding Required” have a three
wire cord and three prong grounding plug. The
plug must be connected to a properly grounded
outlet (See Figure A). If the tool should electrically
malfunction or break down, grounding provides a
low resistance path to carry electricity away from
the user, reducing the risk of electric shock.
The grounding prong in the plug is connected
through the green wire inside the cord to the
grounding system in the tool. The green wire in the
cord must be the only wire connected to the tool's
grounding system and must never be attached to
an electrically “live” terminal.
Your tool must be plugged into an appropriate out-
let, properly installed and grounded in accordance
with all codes and ordinances. The plug and outlet
should look like those in Figure A.
Double Insulated Tools: Tools with
Two Prong Plugs
Tools marked “Double Insulated” do
not require grounding. They have a
special double insulation system which satisfi es
OSHA requirements and complies with the applica-
ble standards of Underwriters Laboratories, Inc., the
Canadian Standard Association and
the National Electrical Code. Double
Insulated tools may be used in either
of the 120 volt outlets shown in
Figures B and C.
* EFCC - The Electronic Feedback Control Circuit maintains constant speed under varying load conditions.
†
Use MILWAUKEE core bits Cat. No. 48-20-5125 through 48-20-5165. Do not use LHS (Large Hole System) Components with
rotary hammers 5340-20 and 5342-20. The bits could fail, breaking apart at the threaded stud and causing injury and property
damage.
Cat. No.
Volts
AC Amps
No Load
RPM*
Blows/
Minute
Max
Percussion
Drill Bit
Diameter
Max
Percussion
Core Bit
Diameter
†
Chisels
Chisel Shank
Type
5337-20
5337-21
5339-20
5339-21
5340-20
5340-21
5342-20
5342-21
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
14
14
14
14
15
15
15
15
--
--
--
--
125 - 250
125 - 250
125 - 250
125 - 250
975-1950*
975-1950*
975-1950*
975-1950*
975-1950*
975-1950*
975-1950*
975-1950*
--
--
--
--
2" Spline
2" Spline
2" SDS-Max
2" SDS-Max
--
--
--
--
6"
†
6"
†
6"
†
6"
†
See
"Chiseling
and
Chipping"
3/4" Hex
3/4" Hex
SDS-Max
SDS-Max
3/4" Hex with
21/32" Round
3/4" Hex with
21/32" Round
SDS-Max
SDS-Max
SPECIFICATIONS
Grounded tools require a three wire extension
cord. Double insulated tools can use either a two
or three wire extension cord. As the distance from
the supply outlet increases, you must use a heavier
gauge extension cord. Using extension cords with
inadequately sized wire causes a serious drop in
voltage, resulting in loss of power and possible tool
damage. Refer to the table shown to determine the
required minimum wire size.
The smaller the gauge number of the wire, the
greater the capacity of the cord. For example, a 14
gauge cord can carry a higher current than a 16
gauge cord. When using more than one extension
cord to make up the total length, be sure each cord
contains at least the minimum wire size required.
If you are using one extension cord for more than
one tool, add the nameplate amperes and use the
sum to determine the required minimum wire size.
Guidelines for Using Extension Cords
• If you are using an extension cord outdoors, be
sure it is marked with the suffi x “W-A” (“W” in Cana-
da) to indicate that it is acceptable for outdoor use.
• Be sure your extension cord is properly wired
and in good electrical condition. Always replace a
damaged extension cord or have it repaired by a
qualifi ed person before using it.
• Protect your extension cords from sharp objects,
excessive heat and damp or wet areas.
READ AND SAVE ALL
INSTRUCTIONS FOR FUTURE USE.
* Based on limiting the line voltage drop to fi ve volts at
150% of the rated amperes.
EXTENSION CORDS
Recommended Minimum Wire Gauge
For Extension Cords*
Nameplate
Amperes
Extension Cord Length
25' 50' 75' 100' 150'
0 - 2.0
2.1 - 3.4
3.5 - 5.0
5.1 - 7.0
7.1 - 12.0
12.1 - 16.0
16.1 - 20.0
18
18
18
18
16
14
12
18
18
18
16
14
12
10
18
18
16
14
12
10
--
18
16
14
12
10
--
--
16
14
12
12
--
--
--
Fig. B
Fig. C
Fig. A
GROUNDING
WARNING Improperly connecting the
grounding wire can result in the risk of elec-
tric shock. Check with a qualifi ed electrician
if you are in doubt as to whether the outlet is
properly grounded. Do not modify the plug
provided with the tool. Never remove the
grounding prong from the plug. Do not use
the tool if the cord or plug is damaged. If
damaged, have it repaired by a MILWAUKEE
service facility before use. If the plug will not
fi t the outlet, have a proper outlet installed by
a qualifi ed electrician.
ASSEMBLY
WARNING To reduce the risk of injury,
always unplug tool before attaching or remov-
ing accessories or making adjustments. Use
only specifi cally recommended accessories.
Others may be hazardous.
Adjusting the Spade Side Handle (Cat. No. 5337-
20, 5339-20 only)
The spade side handle is provided on demolition
hammers only. Do not use the spade side handle
on Rotary Hammers.
1. Slightly loosen the spade side handle by turning
the spade side handle adjusting knob counter-
clockwise.
2. Rotate the spade side handle to the desired
position. The handle can be moved to the left or
right of the tool, as well as forward or backward.
3. Securely tighten the spade side handle adjusting
knob.
Adjusting the Straight Side Handle
Screw the straight side handle into one of three po-
sitions (top, left side, or right side). Tighten securely.
Installing Bits and Chisels
Installing Hammer Chisels
Always clean and grease the chisel shank before
inserting the chisel into the tool. Inspect the shank
to make sure it is not "mushroomed", as described
in "Maintaining Hammer Chisels". Always make
sure that the chisel is in good working condition
before use.
NOTE: To reduce the risk of damage to the bit lock,
do not use round hex shank bits in the 5337-20.
Only use hex shank bits in this tool.
1. Clean and grease the bit or chisel shank.
2. Pull out the bit lock and rotate it 180°.
3. Insert the bit or chisel into the nose of the tool
(Fig. 1)
NOTE: When using hex (on cat. no. 5337-20) or
hex/round (on cat. no. 5340-20) bits or chisels,
the notch in the shank must face toward the
bottom of the nosepiece of the tool.
4. Lock the bit or chisel by pulling out the bit lock
and rotating it 180°.
5. Pull on the bit or chisel to verify that it is locked
into place.
6. To remove, rotate the bit lock 180° and remove
the bit or chisel.
NOTE: Use caution when handling hot bits and chisels.
1. Clean and grease the bit or chisel shank.
2. Insert the bit or chisel into the nose of the tool.
3. Rotate the bit or chisel slowly until it aligns with
the locking mechanism.
4. Push the bit or chisel into the tool until it locks
(Fig. 2).
5. Pull on the bit or chisel to verify that it is locked
into place.
6. To remove, pull the bit release collar toward the
rear of the tool and remove the bit or chisel.
WARNING To reduce the risk of injury
when hammering with rotation, always use
the straight side handle when using this tool.
Always brace or hold securely.
To reduce the risk of injury when hammering
with or without rotation, wear safety goggles
or glasses with side shields.
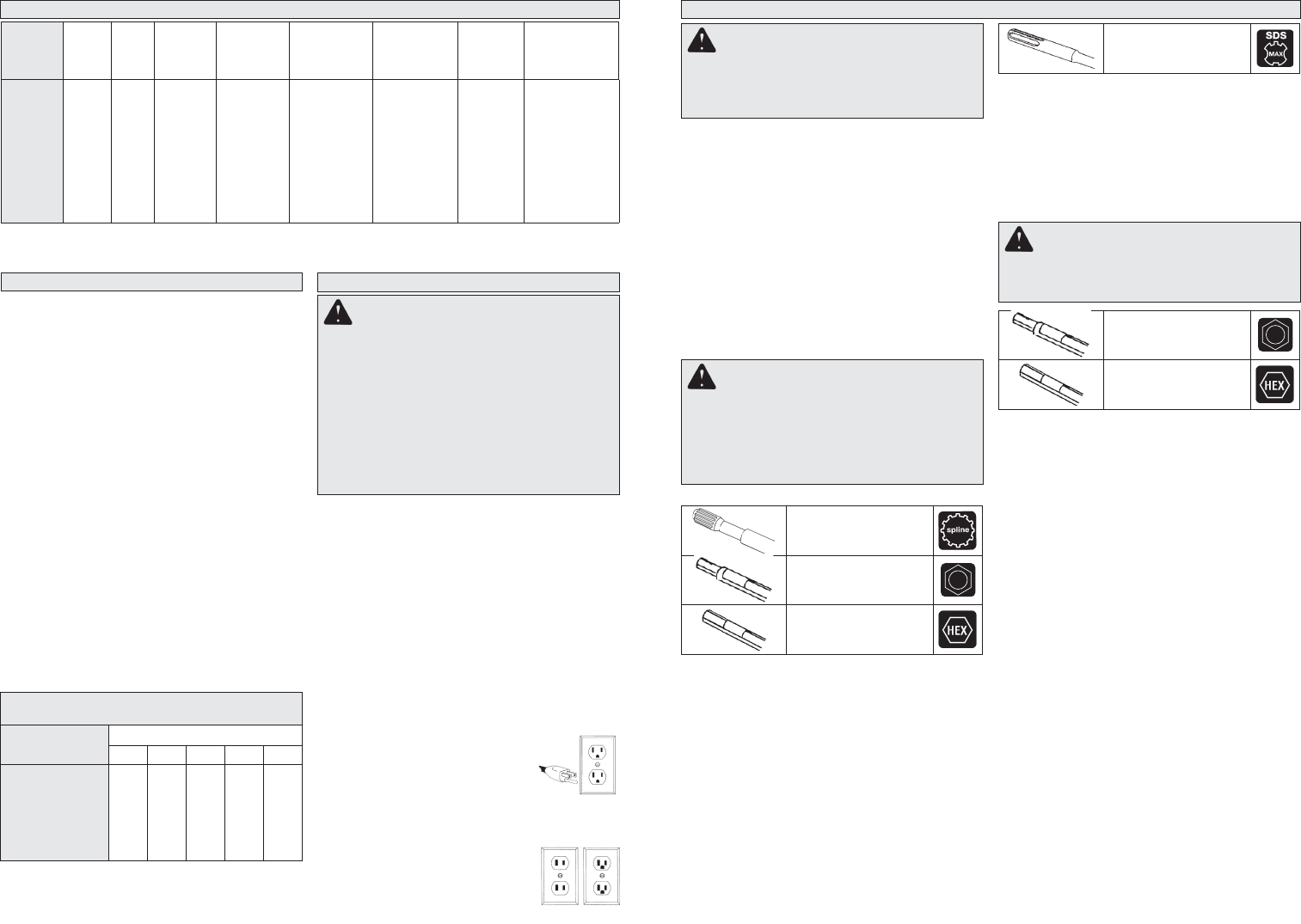
Spline shank
Cat. No. 5340-20 only
Round hex shank
Cat. No. 5340-20 only
Hex shank
Cat. No. 5337-20 only
SDS Max shank
Cat. No. 5339-20,
5342-20
Round hex shank
(Cat. No. 5340-20)
Hex shank
(Cat. No. 5337-20)
WARNING To reduce the risk of
injury, use only specifi cally recommended
MILWAUKEE hammer chisels. Others may
damage tool.


















