-8-
You will extend the life of your bits and do
neater work if you always put the bit in
contact with the work before pulling the
trigger. During the oper a tion, hold the tool
firmly and exert light, steady pressure. Too
much pressure at low speed will stall the tool.
Too little pressure will keep the bit from
cutting and cause excess friction by sliding
over the surface. This can be damaging to
both tool and bit.
DRILLING WITH VARIABLE SPEED
The trigger controlled variable speed feature
will eliminate the need for center punches in
hard materials. The variable speed trigger
allows you to slowly increase RPM. By using
a slow starting speed, you are able to keep
the bit from “wander ing”. You can increase
the speed as the bit “bites” into the work by
squeezing the trigger
DRIVING WITH VARIABLE SPEED
Variable speed drills will double as a power
screwdriver by using a screwdriver bit in the
drill mode. The technique is to start slowly,
increasing the speed as the screw runs
down. Set the screw snug ly by slowing to a
stop. Prior to driving screws, pilot and
clearance holes should be drilled.
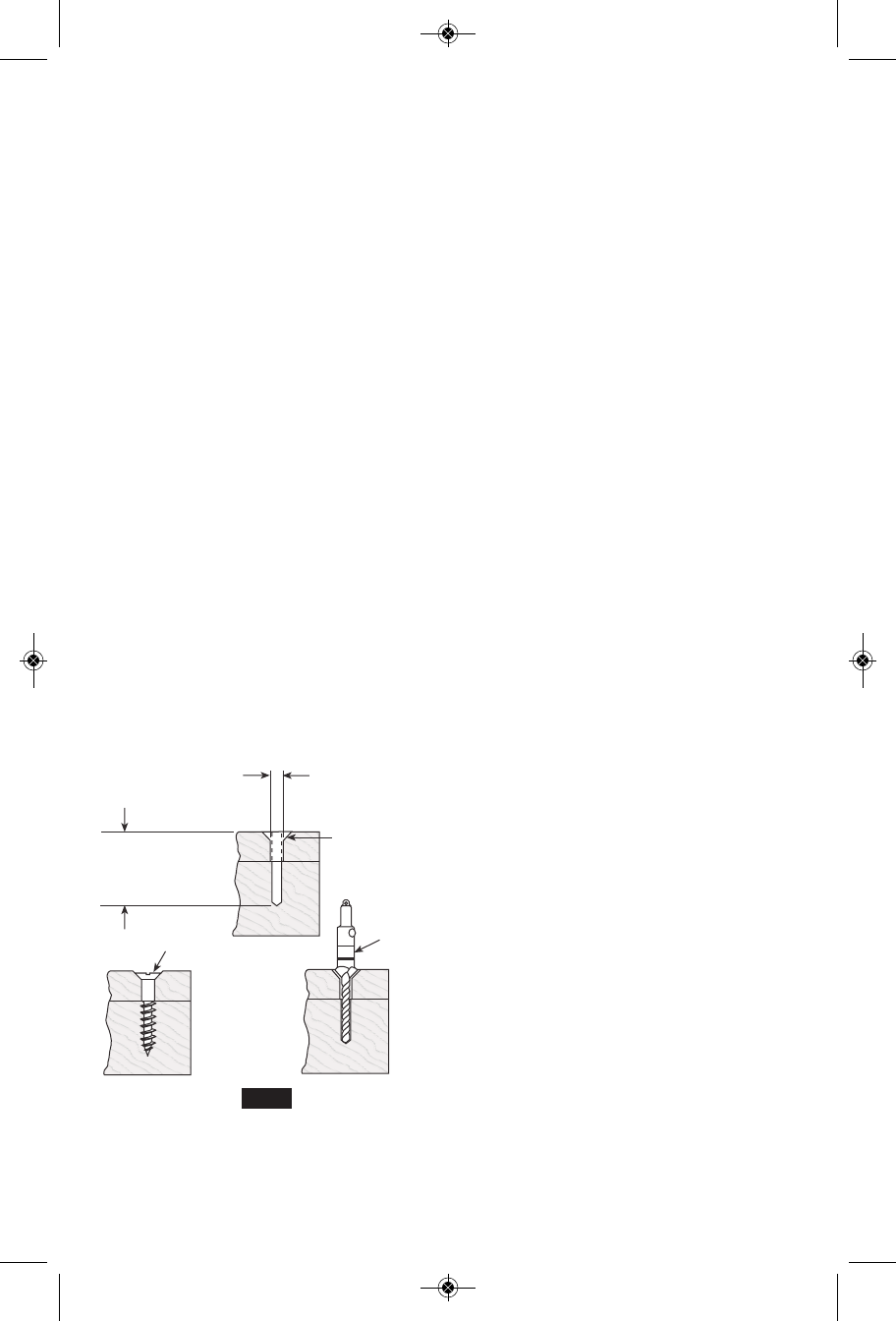
FASTENING WITH SCREWS
This procedure shown in (Fig. 3) will enable
you to fasten ma terials together with your
Drill/Screwdriver without stripping, splitting or
separating the material.
First, clamp the pieces together and drill the
first hole 2/3 the diameter of the screw. If the
material is soft, drill only 2/3 the proper
length. If it is hard, drill the entire length.
Second, unclamp the pieces and drill the
second hole the same diameter as the screw
shank in the first or top piece of wood.
Third, if flat head screw is used, countersink
the hole to make the screw flush with the
surface. Then, simply apply even pressure
when driving the screw. The screw shank
clearance hole in the first piece allows the
screw head to pull the pieces tightly together.
The adjustable screw drill accessory will do
all of these operations quickly and easily.
Screw drills are available for screw sizes No.
6, 8, 10 and 12.
DRILL BITS
Always inspect drill bits for excessive wear. Use
only bits that are sharp and in good condition.
TWIST BITS: Available with straight and
reduced shanks for wood and light duty metal
drilling. High speed bits cut faster and last
longer on hard ma terials.
CARBIDE TIPPED BITS: Used for drilling
stone, con crete, plaster, cement and other
unusually hard nonmetals. Use continuous
heavy feed pres sure when employing carbide
tip bits.
DRILLING WOOD
Be certain workpiece is clamped or anchored
firm ly. Always apply pressure in a straight line
with the drill bit. Maintain enough pressure to
keep the drill “biting”.
When drilling holes in wood, twist bits can be
used. Twist bits may overheat unless pulled out
frequently to clear chips from flutes.
Use a “back-up” block of wood for work that is
likely to splinter, such as thin materials.
You will drill a cleaner hole if you ease up on
the pressure just before the bit breaks through
the wood. Then complete the hole from the
back side.
DRILLING METAL
There are two rules for drilling hard materials.
First, the harder the material, the greater the
pres sure you need to apply to the tool. Second,
the harder the material, the slower the speed.
Here are a couple of tips for drilling in metal.
Lubri cate the tip of the bit occasionally with
cutting oil except when drilling soft metals such
as alu minum, cop per or cast iron. If the hole to
be drilled is fairly large, drill a smaller hole first,
2. Drill same
diameter as
screw shank.
3. Countersink
same diameter
as screw head.
1. Drill 2/3 diameter and
2/3 of screw length for
soft materials, full
length for hard
materials.
Adjustable
Screw
Drill
Screw
Apply a slight
even pressure
when driving
screws.
FASTENING
WITH SCREWS
FIG. 3
Operating Tips
SM 1619X04119 06-09:SM 1619X04119 06-09 6/18/09 1:39 PM Page 8