DC Wiring
975-0012-01-02 Rev A 2–15
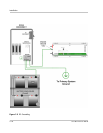
Batteries
The DR Inverter can support either 12-volt battery banks or 24-volt battery banks.
Before proceeding, ensure you have the appropriate sized batteries for this
inverter.
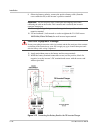
Battery Types
Batteries are available in different sizes, amp-hour ratings, voltage, liquid or gel,
vented or non-vented, chemistries, etc. They are also available for starting
applications (such as an automobile starting battery) and deep discharge
applications. Only the deep discharge types are recommended for inverter
applications. Choose the batteries best suited for the inverter installation and cost.
Use only the same battery type for all batteries in the bank. For best performance,
all batteries should be from the same lot and date. This information is usually
printed on a label located on the battery.
Additional information regarding batteries can be found in the Appendix B,
“Battery Information”.
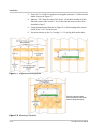
Battery Bank Sizing
The size of the battery bank determines how long the AC loads will operate in a
backup mode without utility power. The larger the battery bank, the longer the run
time. Size the battery bank to the AC load requirements and length of time
required to run from the batteries. In general, the battery bank should not be
discharged more than 50%. Additional DC charging devices such as solar, wind,
hydro, etc., can provide longer run times by recharging the batteries in the absence
of AC utility or generator power.
Additional details on estimating battery bank size and capacity can be found in
“Battery Bank Sizing” on page B–4.
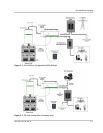
Battery Configuration
The battery bank must be wired to match the inverter’s DC input voltage
specifications (12 Vdc, 24 Vdc, or 48 Vdc). In addition, the batteries can be wired
to provide additional run time. The various wiring configurations are:
• SERIES - Wiring batteries in series increases the total bank output voltage (to
match the inverter’s DC requirements).
• PARALLEL - Wiring the batteries in parallel increases the total run time the
batteries can operate the AC loads.
• SERIES-PARALLEL - Series-parallel configurations increase both the
battery voltage (to match the inverter’s DC requirements) and run-time for
operating the AC loads.
For additional information on how to wire these battery-bank configurations, see
“Battery Configurations” on page B–8.