page 7
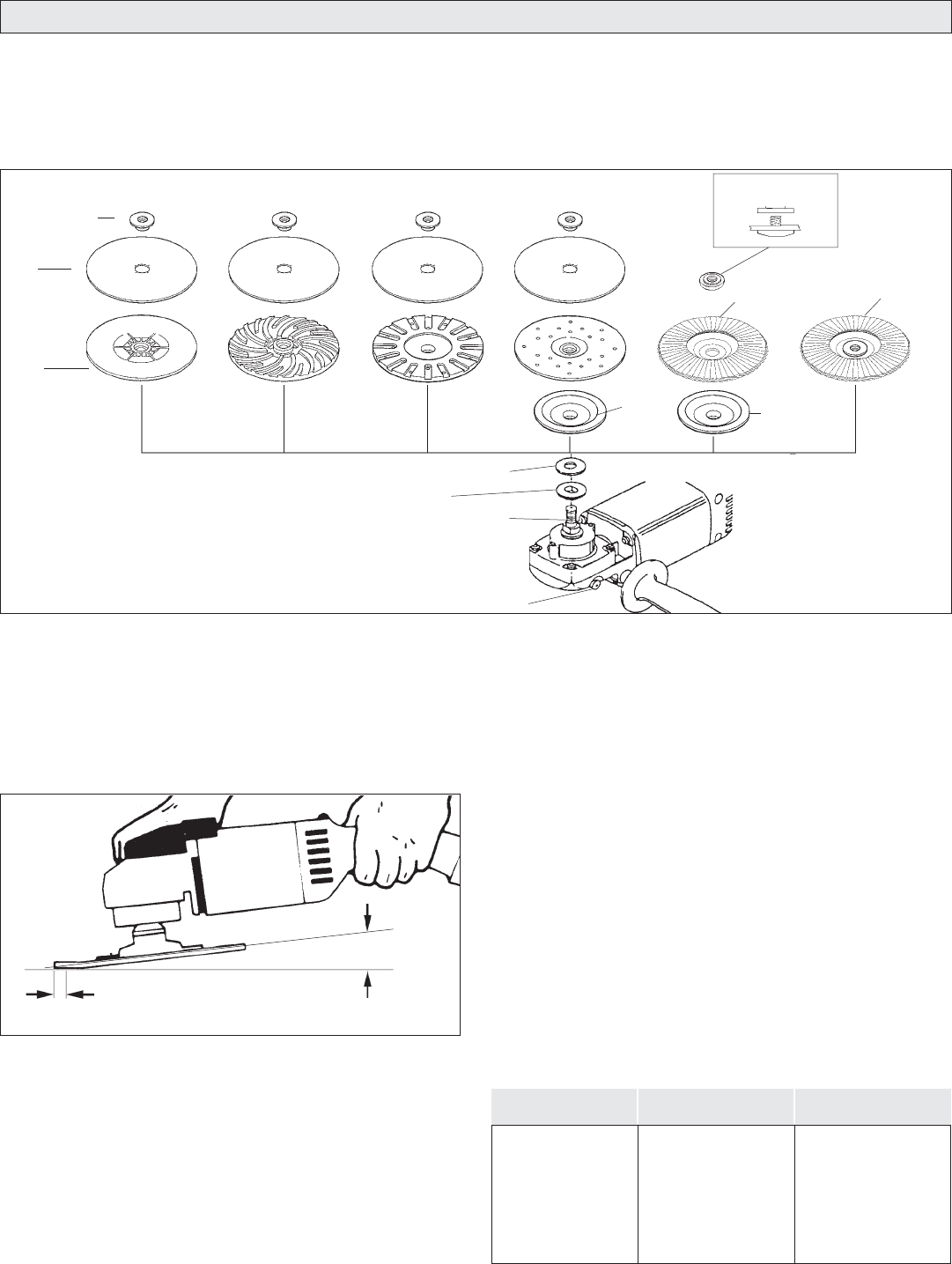
Fig. 3
Hold at a 5° to 15° angle
For best results, use only
this portion of the disc.
Removing Welds or Hammer Marks
When removing welds or hammer marks, limit coarse sanding to the im-
mediate area. Use successively fi ner grits to smooth surface.
Cross Sanding
When fi nishing a surface that has been prepared by a coarse disc or
wheel, sand at right angles to the strokes made by the coarser disc.
Finishing marks left from previous sanding are easily seen and removed for
a uniform fi nish. Failure to cross sand when changing from a coarse disc to
a fi nishing disc may result in deep scratches and circular marks.
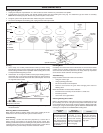
Installing Sanding Discs
1. Unplug tool and place it upside down on a level surface as shown. Remove any accessories from spindle.
2. Thread fl ange and nylon washer onto spindle. Attach backing pad and sanding disc using Fig. 2 to determine type and order of assembly.
NOTE: When installing fl ap disc without hub, position fl ap disc nut as shown.
3. To tighten, press in the spindle lock button while turning disc nut clockwise.
4. To remove sanding disc and backing pad, unplug tool and reverse procedure.
3. Use long, sweeping, side to side strokes, advancing forward to produce
the desired fi nish.
USING SANDING DISCS
Selecting Sanding Discs & Grit
Refer to the table below to select the correct type of sanding disc for your
job. Generally, use 16, 24 or 36 grit for heavy stock removal; 50, 60 or 80
grit for medium stock removal and 120 grit for fi nishing. Always begin with
a coarse grit, using successively fi ner grits to obtain the desired fi nish. See
Catalog for a complete list of MILWAUKEE sanding discs.
Finishing Metal
Constantly move across the surface. Work faster on curved surfaces where
contact areas are smaller and pressure is greater. Flat areas may appear
at the end of the stroke when pressure is too heavy. Ease up on pressure
at end of each stroke and when reversing strokes.
Troubleshooting
Deep scratches and circular marks can result from:
• Using too coarse a grit
• Using a partially glazed disc
• Dirt or loose metal on the workpiece
• Failure to sand across the grain when changing from coarse to
fi nishing discs
Bluish discoloration of metal surface indicates:
• Excessive heat caused by circular motion in a small area
• Excessive pressure
• Use of worn out or glazed discs
Ceramic
Aluminum
Zirconia Bi-Cut
Aluminum
Oxide
For fast cutting,
general purpose discs
for most metal jobs.
Best for cold-rolled
steel, stainless steel or
metals requiring tough,
fast cutting, long last-
ing abrasives.
Lasts up to 3 times
longer than aluminum
oxide discs. For general
metal working. Ideal for
tough jobs.
Unique grit pattern is
arranged in clus-
ters for faster stock
removal and cleaning.
Ideal for removing paint
from cars, boats, etc.
without clogging.
Fig. 2
Backing
pads
A. Polypropylene
B. Spiral
C. Rubber
D. Phenolic
Disc nut
Sanding
disc
Rubber
pad
Type 27
fl ange
Flap disk
without hub
Flap disk
with hub
BCD
A
Sanding
1. Use a clamp, vise or other practical means to hold your work, freeing
both hands to control your tool. Firmly grasp rear handle and side handle
before starting and while tool is in operation. Allow sanding disc to come
to full speed before beginning to sand.
2. Hold tool at 5° to 15° angle as shown to ensure proper sanding pressure
and control (Fig. 3). Too great an angle will result in too much pressure
and could cause excessive wear to the disc and workpiece. Too small
an angle will reduce control.
Spindle
Nylon washer
Spindle lock button
Flange
Flap disc nut
position