page 11
Recommended Materials and Applications
The following materials can be cut with the compound miter saw. There
are many types of saw blades available. Always use the proper blade
for the particular material and application.
Wood
solid wood, plywood, particle board, MDF (medium density fiber-
board), HDF (high density fiberboard), melamine laminated particle
board, formica laminates, hardboard (masonite).
Plastics
PVC, CPVC, ABS, solid surfacing materials (such as Corian
®
), and
other plastic materials.
Nonferrous Metals
aluminum, brass, copper, and other non-ferrous materials.
APPLICATIONS
Cutting Non-Square Materials
Cutting Round (Cylindrical) Materials
"V" shaped blocks can be used to support round materials like closet rod
and plastic pipe.
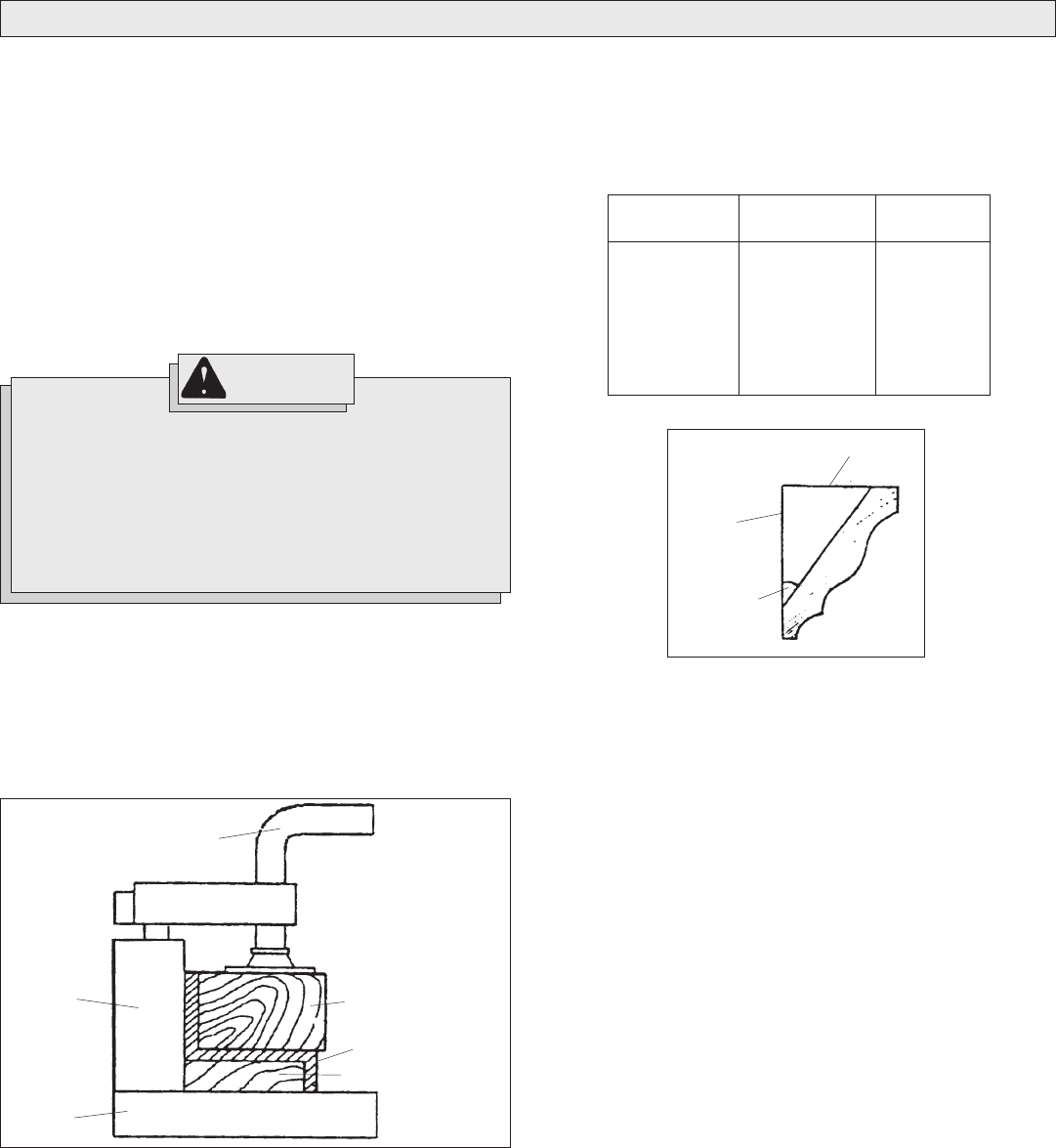
Aluminum Sash and Other Channel Type and Materials (Fig. 9)
Aluminum sash material can be supported with blocks to prevent it from
deforming while it is being cut (Fig. 9).
WARNING!
Do not cut stone, brick, concrete, or ferrous metals (iron,
steel, stainless steel, or alloys of these metals) with this
saw.
Do not use abrasive wheels with this saw.
Dust created by cutting these materials and/or using abra-
sive cut-off wheels can jam the blade guard and possibly
cause personal injury.
Cutting Compound Miters (Fig. 10)
The chart below identifies miter and bevel settings for various types of
crown molding for 90° corners. Note that these are ideal settings and
may vary because many moldings have slightly different spring angles
and some walls are not perfectly square. Fig. 10 illustrates the relation-
ship between the spring angle, the ceiling, the wall and the molding.
Type of Crown
(spring angle)
30°
35°
38°
40°
45°
52°
Miter
(angle of table)
26.6°
29.8°
31.6°
32.7°
35.3°
38.2°
Bevel
(tilt of blade)
37.8°
35.4°
33.9°
32.8°
30°
25.8°
* Wood is positioned flat on the miter saw table.
Fig. 10
Ceiling
Wall
Spring
angle
Fig. 9
Clamp
Fence
Base
Wood support block
Aluminum material
Wood support block


















