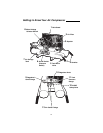
10
Thermal Overload Protector
If thermal overload protector shuts motor
OFF frequently look for the following
causes.
1. Low voltage.
2. Wrong gauge wire.
3. Clogged air filter.
4. Lack of proper ventilation.
5. Unit is being used with an extension
cord.
See Troubleshooting Chart for corrective
action.
This compressor is equipped
with an automatic reset thermal
overload protector which will
shut off motor if it becomes
overheated.
!
CAUTION:
The motor must be allowed to
cool down before start-up is
possible. The motor will auto-
matically restart without warn-
ing if left plugged into electrical
outlet, and the motor is turned
on.
!
CAUTION:
ASME Safety Valve
A safety valve that automatically releases
the air if the air receiver (tank) pressure
exceeds the preset maximum.
PSI (Pounds per Square Inch)
Measurement of the pressure exerted by
the force of the air. The actual psi output
is measured by a pressure gauge on the
compressor.
SCFM (Standard Cubic Feet per
Minute)
Sometimes called CFM (Cubic Feet per
Minute). Measurement of air volume
delivered by the compressor.
Air Delivery
A combination of psi and SCFM. The air
delivery required by a tool is stated as
(number) SCFM at (number) psi. The
combination of these figures determines
what size unit is needed.
Air Tank Capacity
The volume of air stored in the tank and
available for immediate use. A large tank
allows the intermittent use of an air tool
with an air requirement higher than the
compressor’s rated delivery.
Volts or Voltage
A measurement of the force of an electri-
cal current.
Amps or Amperage
A measure of the electrical force minus
the resistance on an electrical line.
RIDGID air compressors require 15
amps for operation. Be sure the com-
pressor will operate on an electrical line
with the proper amps. If other appliances
operate on the same line, they will
reduce the available amps. If the amper-
age is not adequate, the result will be
blown fuses or tripped circuits.
Glossary of Terms
Motor Specifications and
Electrical Requirements (continued)