90-0115-00
10/97 Fltman.pm65
TROUBLESHOOTING
1. Digital clocks either employ an internal time
base or derive their time base from the incoming
AC waveform. The frequency is usually well
regulated at 60 Hz. The clock either counts the
number of peaks in the waveform or the number
of times the waveform crosses zero volts. The
circuitry to count the zero crossing events is more
popular. The longer zero cross time of the
inverter's modified sinewave may cause double
clocking, resulting in a faster clock.
Slow
Digital
Clock
36
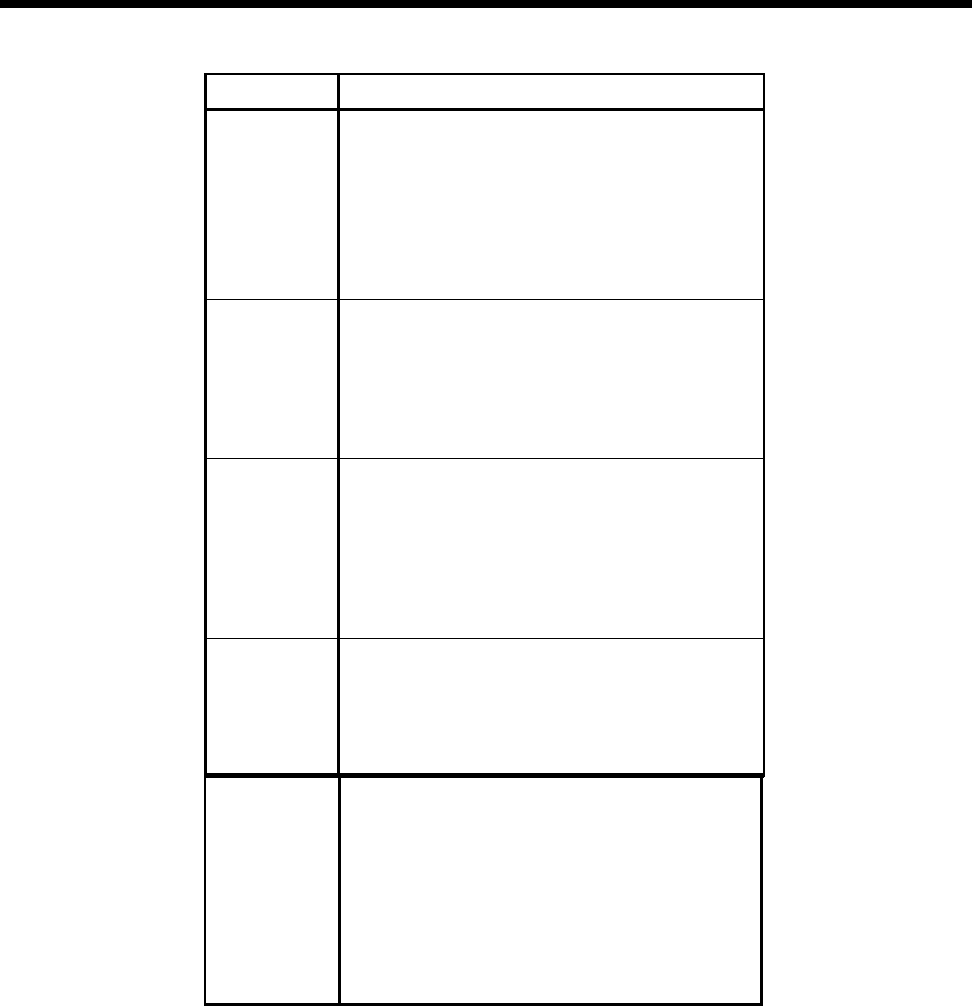
Problem Things to Check
No Inverter
Output
1. Battery voltage under load.
2. Battery connections and DC fuse.
3. Circuit breaker on front panel.
4. Thermal condition, high powered loads or
inadequate ventilation may cause overheating.
5. Overloads or short circuit, check for excessive
loads or bad wiring connections.
6. Reset button oin GFCI outlet.
Low Inverter
Output Voltage
Confirm that your volt meter is a true RMS meter.
Standard volt meters will not accurately read the
waveform of the inverter and may read anywhere
from 90 to 120 volts. If a true RMS meter is not
available, check the brightness of an incandescent
light bulb - if it appears normal, the output voltage is
properly regulated.
Little or No
Output from
Battery
Charger
1. Wiring connections - check both the AC and DC
connections.
2. AC input voltage - low voltage input will result in
low DC output current. Expect reduced charger
output from generators under 3,500 watts.
3. AC reverse polarity - check for voltage between
the incoming white and green wires. If 120 volts is
measured, this is reverse polarity.
Microwave
Oven Cooking
Slow
1. Microwave ovens will normally cook slow on
inverters due to a slightly low peak AC voltage. 2.
Cooking speed will be determined by battery
voltage. Low voltage results in increased cooking
time. Support the battery bank with an alternator or
other charging source for quicker cooking.