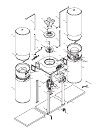
-14- G9958 4 H.P. Dust Collector
the removal of particulate matter, especially saw-
dust, since it is durable and completely flexible.
Polyethylene is also very economical and avail-
able in a wide variety of diameters and lengths for
most applications.
PLASTIC DUCT
The popularity of plastic duct is due to the fact that
it is an economical and readily available product.
It is also simple to assemble and easily sealed
against air loss. The primary disadvantage of
plastic duct for dust collection, whether black ABS
or white PVC and even rubber or polyethylene
flex-hose, is the inherent danger of static electri-
cal build-up.
Since plastic hose is abundant, relatively inex-
pensive, easily assembled and air tight, it is a very
popular material for conveying dust from wood-
working machines to the dust collector. We rec-
ommend using flexible hose (flex-hose) to con-
nect the woodworking machine to the dust collec-
tor. However, plastic flex-hose and plastic duct
are an insulator, and dust particles moving
against the walls of the plastic duct create a stat-
ic electrical charge build up. This charge will build
until it discharges to a ground. If a grounding
medium is not available to prevent static electrical
charge build up, the electrical charge will arc to
the nearest grounded source. This electrical dis-
charge may cause an explosion and subsequent
fire inside the system.
To protect against static electrical charge build up
inside a non-conducting duct, a bare copper wire
should be placed inside the duct along its length
and grounded to the dust collector. You must also
confirm that the dust collector is continuously
grounded through the electrical circuit to the elec-
tric service panel.
If you connect the dust collector to more than one
machine by way of a non-conducting branching
duct system and blast gates, the system must still
be grounded as mentioned above. We recom-
mend inserting a continuous bare copper ground
wire inside the entire duct system and attaching
the wire to each grounded woodworking machine
and dust collector.
Be sure that you extend the bare copper wire
down all branches of the system. Do not forget to
connect the wires to each other when two branch-
es meet at a Y or T connection. Use wire nuts.
Ensure that the entire system is grounded. If
using plastic blast gates to direct air flow, the
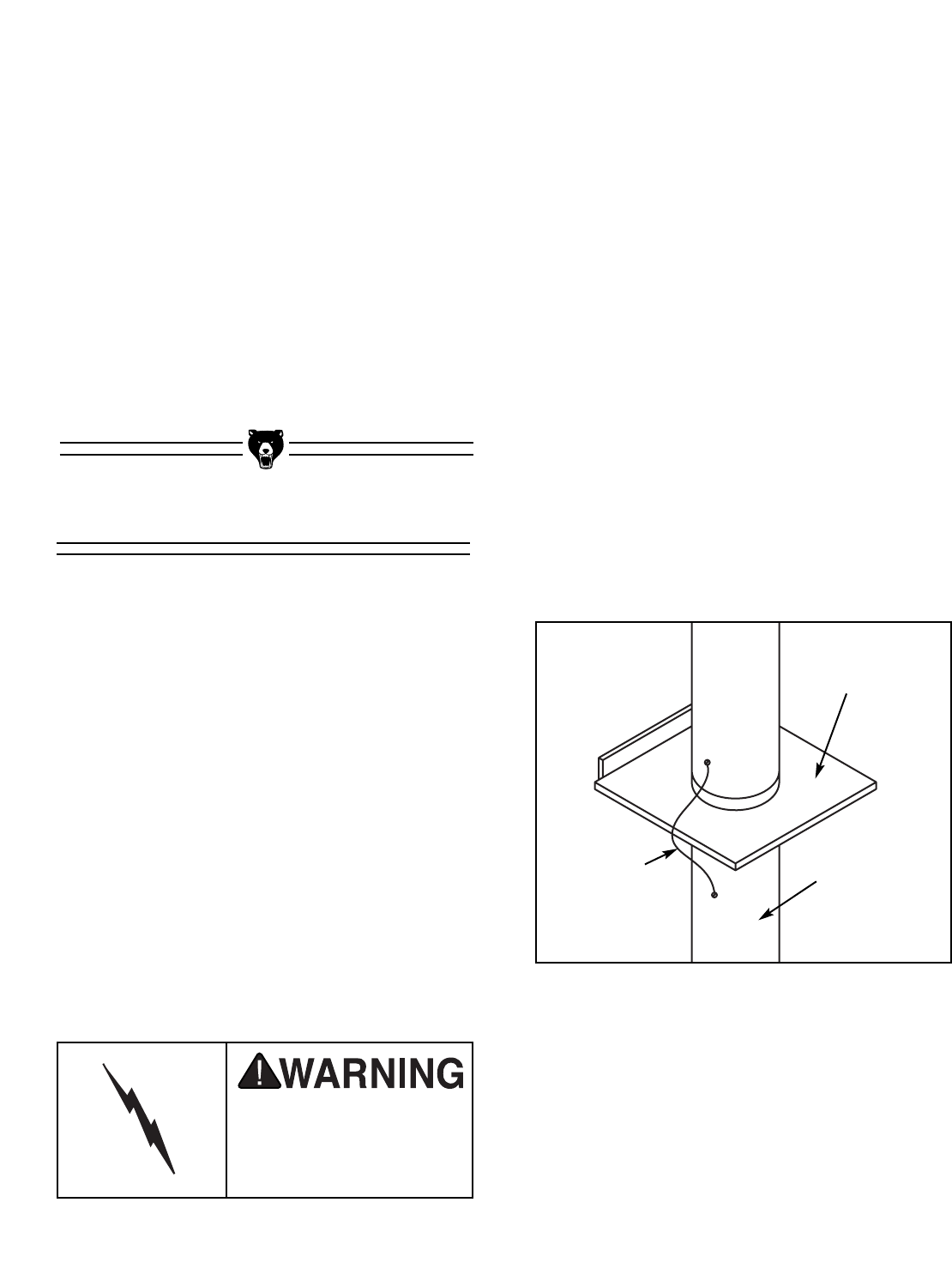
grounding wire must be jumped (Figure 12)
around the blast gate without interruption to the
grounding system.
System Grounding
We also recommend wrapping the outside of all
plastic ducts with bare copper wire to ground the
outside of the system against static electrical
charge build up. Wire connections at Y’s and T’s
should be made with wire nuts.
Figure 12. Ground jumper wire when using plas-
tic blast gates and metal duct.
Plastic Blast Gate
Metal Duct
Copper Ground Wire
Guard against static
electric build up.
Ground all dust collec-
tion hose and pipe.