stainless steel brush to eliminate any
oxides on the weld and grounding
surface. 100% Argon must be used
when welding aluminum. If Argon is not
used, metal penetration is unlikely.
1. Verify that welder is OFF and power
cord disconnected.
2. Remove welder cover to expose the
ON/OFF switch.
9
WG4000
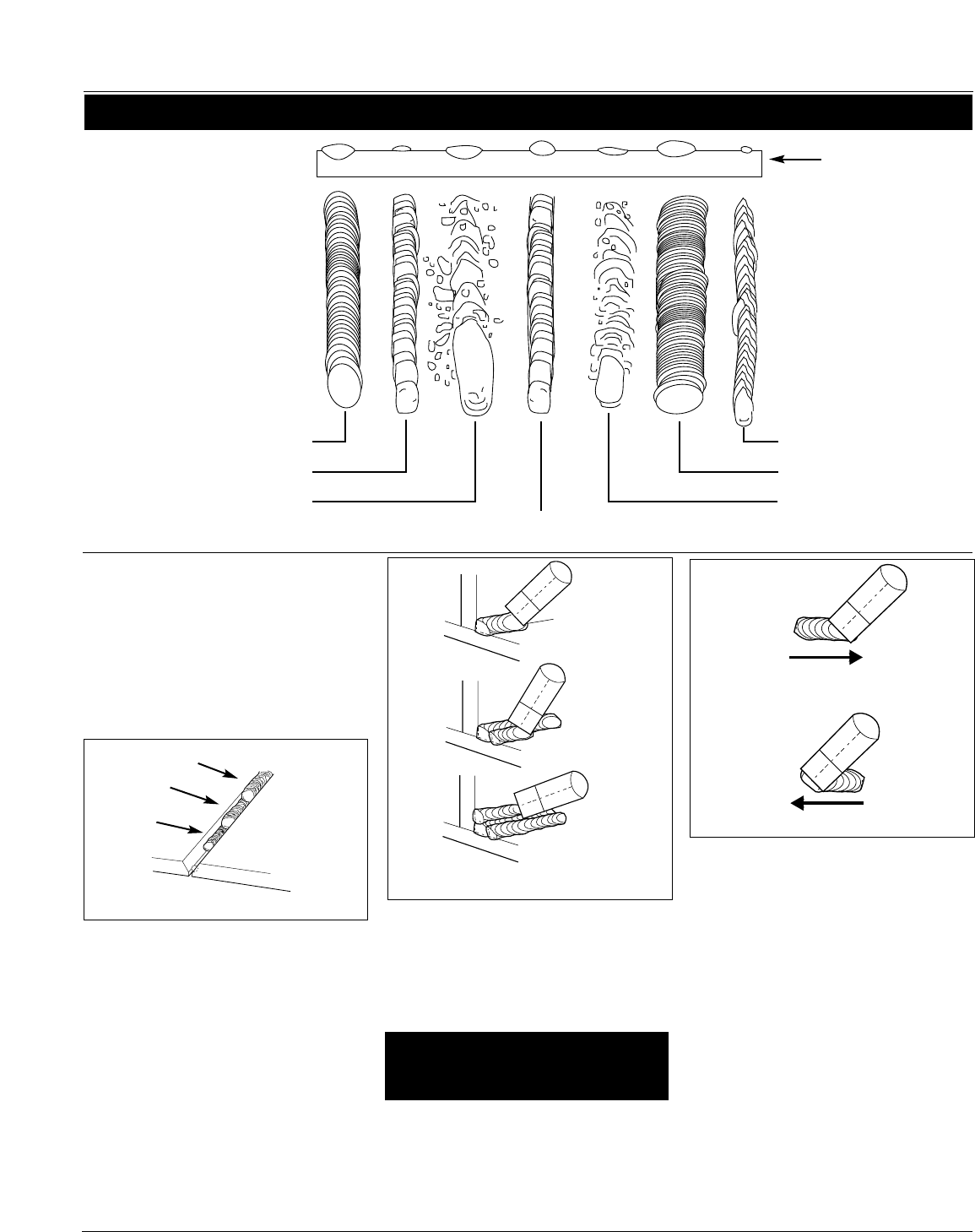
Normal Heat, Wire Speed, Travel
Speed
Heat Too Low
Heat Too High
Wire Speed Too Fast
Wire Speed Too Slow
Travel Speed Too Slow
Travel Speed Too Fast
Base Metal
Figure 12 - Weld Appearance
Figure 14 - Multiple Weld Passes
Welding Guidelines
(Continued)
WELD PASSES
Sometimes more than one pass is
necessary to fill the joint. The root pass
is first, followed by filler passes and
the cover pass. If the pieces are thick, it
may be necessary to bevel the edges
that are joined at a 60º angle.
NOTE: Remember to remove the slag
before each pass for gasless process.
PUSH VS PULL TECHNIQUE
The type and thickness of the work
piece dictates which way to point the
gun nozzle. For thin materials (18 gauge
and up) and all aluminum, the nozzle
should point out in front of the weld
puddle and push the puddle across the
workpiece. For thicker steel, the nozzle
should point into the puddle to increase
weld penetration. This is called
backhand or pull technique
(See Figure 15).
ALUMINUM WELDING
Any aluminum surface to be welded,
must be cleaned thoroughly with a
Figure 13 - Weld Passes
Cover
Filler
Root
3. Disconnect the black and white
power cord wires connected to the
ON/OFF switch.
4. Disconnect the green power cord
wire connected to welder frame.
5. Loosen the cord strain relief screw(s)
and pull cord out of strain relief.
6. Install new cord in reverse order.
PUSH
PULL
Figure 15
Supply Cable
Replacement
www.chpower.com