15
4. Bed ways; keep clean, use steel wool to
remove any rust spots, and apply paste wax to
prevent buildup of rust and finishes.
5. Tool rest; use a mill file to remove nicks and
dings.
6. Spindle tapers; should be clean and free of
dust and chips for proper seating of tapers.
7. Tailstock; clean and lubricate quill and locking
device.
8. Lighting; proper lighting is essential to
eliminate shadows and reduce eye strain.
10.2 Turning Tools
If possible, select only quality, high-speed steel
turning tools. High-speed steel tools hold an edge
and last longer than ordinary carbon steel. As one
becomes proficient in turning, a variety of specialty
tools for specific applications can be acquired. The
following tools provide the basics for most
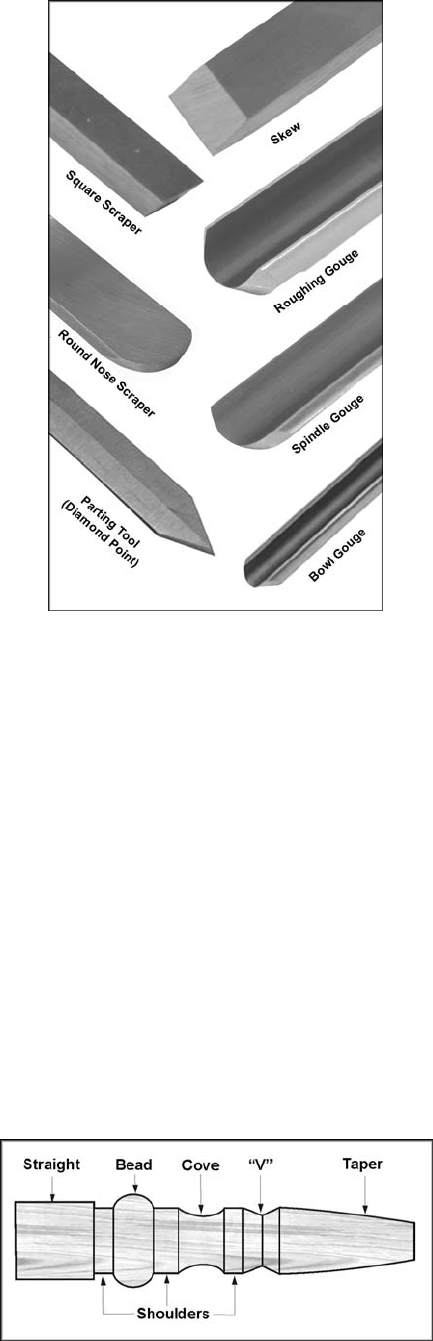
woodturning projects (see Figure 21):
Skews – 1-1/2" and 1" or 1-1/4", used to make
finishing cuts and details.
Large Roughing Gouge – 1" to 1-1/4", used to
eliminate waste wood.
Spindle Gouges – 1/4", 3/8", 1/2", used to turn
beads, coves and other details.
Deep Fluted Bowl Gouge – 1/4", 3/8" and 1/2",
used for turning bowls & plates.
Square Scraper (Bedan) – 3/8” or 1/2", used to
create square shoulders.
Large Round Nose (Domed) Scraper – 1-1/2",
used to reduce ridges on interior of bowls, round
edges of bowls, etc.
Parting Tool - 1/8", used for scraping, making a
cut-off, or to set diameters for sizing.
For safety and best performance, keep tools sharp.
If a tool stops cutting or requires excessive
pressure to make a cut, it needs to be sharpened.
A number of brand name sharpening jigs and
fixtures are available; however, a woodturner
should learn to sharpen tools freehand.
For best results, use a slow speed grinder (1800
rpm) fitted with a 60-grit aluminum oxide wheel (for
shaping) and a 100-grit alum. oxide wheel (for final
sharpening and touchup). The grinder should be
located near your lathe and at a comfortable
height. A diamond dresser will keep the wheels
true and eliminate glazing.
Never allow the tool to rest in one place on the
wheel, keep it moving and use a light touch.
Figure 21
Basic Turning Tools
Carbon steel tools can overheat easily and should
be cooled frequently. If the edge turns blue, it has
lost its temper and should be ground past the blue
area. High-speed steel tools are not as likely to
overheat, but can be damaged if allowed to get red
hot. High-speed steel tools should not be
quenched for cooling. Honing with a diamond lap
or slipstone will save trips to the grinder and keep
the edge fresh.
10.3 Spindle Turning
Spindle turning takes place between the centers of
the lathe. It requires a spur or drive center in the
headstock and a live or dead center in the tailstock.
A cup center rather than a cone center in the
tailstock will often reduce the risk of splitting the
stock.
Figure 22 shows the basic profile shapes in spindle
turning.
Figure 22


















