22
MAC 500/E User Manual
Replacing fuses
The MAC 500/E has 4 fuses. The main fuse is located on the power-switch panel and may be replaced without opening
the fixture.
The fuses for each of the 3 low-voltage power supplies are located on the printed circuit board. If one of the circuit
board LEDs does not light, one of these fuses may be blown.
1. Remove the printed circuit board.
2. Locate and replace the defective fuse with one of the same rating. The fuses are shown on the
PCB layout diagram and their values are listed in the specifications.
3. Replace the printed circuit board.
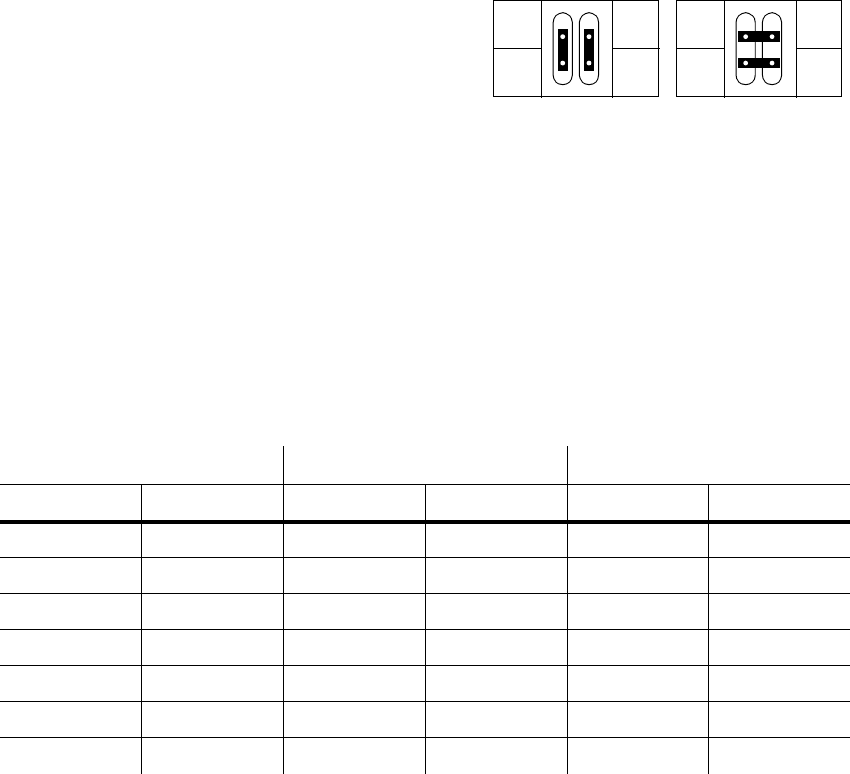
Changing the XLR pin-out
1. Remove the printed circuit board.
2. Position the jumpers for the desired XLR pin-out
as shown.
3. Replace the printed circuit board.
Changing voltage and frequency settings
7KHYROWDJHDQGIUHTXHQF\VHWWLQJVPXVWPDWFKWKHORFDO$&SRZHUVXSSO\ These settings are printed on the serial
number label on the bottom of the base. If the voltage is not within 5 percent of the local supply or the frequency (50/
60 Hz) is different, then the magnetic ballast and/or transformer must be rewired.
MAC 500 with magnetic ballast
1.
Disconnect the MAC 500 from AC power.
Remove the top covers.
2. Find the correct transformer and ballast terminals for your AC supply in the table below. Consult
a qualified electrician if you do not know the AC frequency and voltage.
3. Locate the transformer: it is on the left end, near the power switch. Move the BROWN and RED
transformer wires to the correct terminal. The terminal number is printed in front of the connec-
tion tab.
4. Locate the magnetic ballast: it is on the opposite end from the transformer, near the control
panel. Move the BROWN ballast wire to the correct terminal. The terminal number is printed in
front of the connection tab.
5. Replace the top covers before applying power.
2
3+
-
2
3+
-
DMX pin-outMartin pin-out
(default)
AC Supply Transformer Magnetic Ballast
Frequency Voltage Voltage Terminal Setting Terminal
50 Hz 200-210 V 210 V 4 200 V / 50 Hz 7
50 Hz 210-220 V 210 V 4 230 V / 50 Hz 10
50 Hz 220-235 V 230 V 6 230 V / 50 Hz 10
50 Hz 235-240 V 230 V 6 245 V / 50 Hz 12
50 Hz 240-260 V 250 V 8 245 V / 50 Hz 12
60 HZ 200-217 V 210 V 4 208 V / 60 Hz 4
60 HZ 217-240 V 230 V 6 227 V / 60 Hz 7
