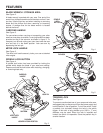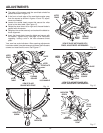
6
GLOSSARY OF TERMS FOR WOODWORKING
RULES FOR SAFE OPERATION
THIS TOOL shall have the following markings:
a) Wear eye protection.
b) Keep hands out of path of saw blade.
c) Do not operate saw without guards in place.
d) Do not perform any operation freehand.
e) Never reach around saw blade.
f) Turn off tool and wait for saw blade to stop before
moving workpiece or changing settings.
g) Disconnect power (or unplug tool as applicable)
before changing blade or servicing.
h) No load speed.
ALWAYS carry the saw only by the carrying handle.
AVOID direct eye exposure when using the laser guide.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS. Refer to them frequently
and use them to instruct other users. If you loan someone
this tool, loan them these instructions also.
WARNING:
Some dust created by power sanding, sawing,
grinding, drilling, and other construction activities
contains chemicals known to cause cancer, birth
defects or other reproductive harm. Some examples
of these chemicals are:
• lead from lead-based paints,
• crystalline silica from bricks and cement and
other masonry products, and
• arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated
lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending
on how often you do this type of work. To reduce
your exposure to these chemicals, work in a well
ventilated area and work with approved safety equip-
ment, such as those dust masks that are specially
designed to filter out microscopic particles.
Arbor
The shaft on which a blade or cutting tool is mounted.
Bevel Cut
A cutting operation made with the blade at any angle other
than 90˚ to the miter table.
Compound Miter Cut
A compound miter cut is a cut made using a miter angle and
a bevel angle at the same time.
Crosscut
A cutting or shaping operation made across the grain of the
workpiece.
Freehand
Performing a cut without using a fence, vise, fixture, work
clamp, or other proper device to keep the workpiece from
twisting or moving during the cut.
Gum
A sticky, sap based residue from wood products.
Miter Cut
A cutting operation made with the blade at any angle other
than 90˚ to the fence.
No Hands Zone
Area between the marked lines on the left and right side of
the miter table base. This zone is identified by no hands zone
labels placed inside the marked lines on the miter table base.
Resin
A sticky, sap base substance that has hardened.
Revolutions Per Minute (RPM)
The number of turns completed by a spinning object in one
minute.
Saw Blade Path
The area over, under, behind, or in front of the blade. As it
applies to the workpiece, that area which will be, or has been,
cut by the blade.
Set
The distance that the tip of the saw blade tooth is bent (or set)
outward from the face of the blade.
Through Sawing
Any cutting operation where the blade extends completely
through the thickness of the workpiece.
Throw-Back
Throwing of a workpiece in a manner similar to a kickback.
Usually associated with a cause other than the kerf closing,
such as a workpiece not being against the fence, being
dropped into the blade, or being placed inadvertently in
contact with the blade.
Workpiece
The item on which the cutting operation is being done. The
surfaces of a workpiece are commonly referred to as faces,
ends, and edges.
Zero Clearance Throat Plate
A plastic throat plate inserted in the miter table that allows for
blade clearance. When you make your first cut with your
compound miter saw, the saw blade cuts a slot through the
throat plate the exact width of the blade. This provides for a
zero clearance kerf that minimizes workpiece tear-out.