13
4. Tighten both handles securely.
To avoid trapping the
workpiece or fingers between the table and
abrasive disc, the table edge should be
positioned a maximum of 1/16” from the
abrasive disc.
Use of the Miter Gauge
The miter gauge is used to sand accurate
angles on workpieces. When using the miter
gauge on the horizontal table position, you can
sand a single angle. By tilting the disc table and
using the miter gauge in combination with the
table tilted, it is possible to sand compound
angles as well.
The miter gauge rotates to 30° for bevel
sanding. Loosen the knob and rotate the gauge
body until the pointer lines up with the desired
angle on the scale.
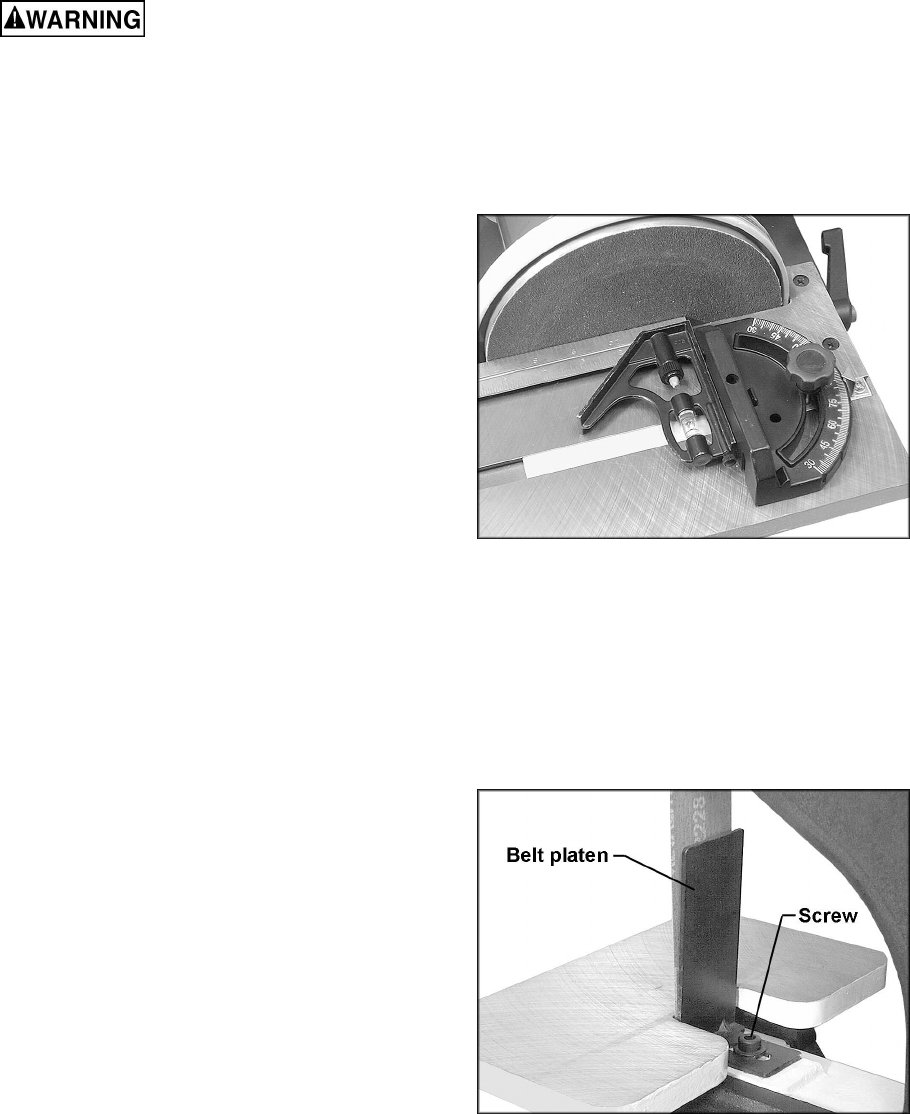
Use a square to confirm that the miter gauge is
set at 90° (perpendicular to the disc). See Figure
12. If slight adjustment is needed:
1. Loosen the knob.
2. Adjust the miter gauge body until it is flush
with the square, and the square is flush with
the disc.
3. Tighten the knob.
4. Loosen the screw on the pointer and adjust
the pointer until it aligns with 90° on the
scale.
5. Tighten the screw on the pointer.
Belt Platen
The belt platen (Figure 13) is used to properly
support the workpiece while sanding. The platen
is constructed of heavy steel to provide
adequate support.
The platen should be adjusted so it is almost
touching the back of the abrasive belt. Loosen
the socket head cap screw and adjust the platen
to the desired position. Tighten the screw to
secure the platen.
The platen can be removed for operations such
as stripping, contour sanding, polishing or other
special operations. To remove the platen,
remove the socket head cap screw and washer.
Be sure to re-install the platen to perform
operations where support of the belt is required.
Figure 12
Figure 13