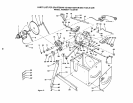
TROUBLE SHOOTING
WARNING: FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY, TURN SWITCH "OFF" AND ALWAYS REMOVE PLUG FROM POWER SOURCE
OUTLET BEFORE TROUBLESHOOTING.
TROUBLE SHOOTING -- GENERAL
TROUBLE PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
Excessivevibration. 1. Discard Blade and usea different blade.
2. See "Getting To Know Your Saw"
section, "Tilt Lock Knob"
1.See "Adjustments" section "Miter Gauge".
1.Sharpen or replace blade.
Cannot make square
cut when crosscutting.
Cut binds, burns or
stalls motor when
ripping.
•Cut not true at 90°
or 45 ° positions.
"Tilt crank and
elevating hand
wheel turn hard.
1. Blade out of balance.
2. Failure to tighten
Tilt Lock Knob.
1. Miter gauge not adjusted
properly.
1. Dull blade with improper
tooth set.
2. Blade is Heeling.
3. Warped board.
4. Rip fence not parallel to
blade.
5. Spreader out of
alignment
1. Stop screws not properly
adjusted.
1. Tilt lock knob not
loosened when making
tilt adjustment.
2. Gears worms and
teeth clogged with
sawdust.
2. See "Adjustments" section, "Heeling Adjustments..."
3. Make sure concave or hollow side is facing
"down," feed slowly.
4. See "Assembly" section, "Aligning Rip Fence"
5. See "Assembly" section, "Installing
BladeGuard."
1. See "Adjustments" section, "Blade Tilt, or Squareness
Blade to Table."
1. See "Getting To Know Your Saw" section,
"Tilt Lock Knob."
2. See "Lubrication" section.
TROUBLE SHOOTING -- MOTOR
NOTE: Motors used on wood-working tools are particularly
susceptible to the accumulation of sawdust and wood chips
and should be blown out or "vacuumed" frequently to
prevent interference with normal motor ventilation.
TROUBLE PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
Excessive noise. 1. Motor. 1. Have motor checked by qual ified service
technician. Repair service is available at
your nearest Sears store.
1. 1. Do not use other appliances or motors on
same circuit when using the saw.
Motor fails to develop
full power. (Power
output of motor decreases
rapidly with decrease in
voltage at motor terminals.
For example, a reduction
of 10% in voltage causes
a reduction of 19% in
maximum power output
of which the motor is
capable, while areduction
of 20% in voltage causes
areduction of 36% in
maximum power output.)
Circuit overloaded with
lights, appliances and
other motors.
Undersize wires or circuit
too lon_
2.
3. General overloading of
power company
facilities. (In some
sections of the
country, demand for
electrical power may
exceed the capacity
of existing generating
and distribution systems.)
4. Incorrect fusesor circuit
breakers in power line.
2. Increasewire sizes,or reduce length of wiring.
See "Motor Specification and Electrical
Requirements" section.
3. Request avoltage check from the power company.
4. Install correct fuses or circuit breakers.
28