1414
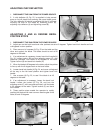
ADJUSTING BLADE GUARD
After an extended period of time the movable blade guard (A)
Fig. 30, might become sloppy and move erratically when the
cuttinghead is lowered. This can be easily corrected by
slightly tightening nut (B) until the lower blade guard (A)
moves smoothly.
TYPICAL OPERATIONS AND HELPFUL HINTS
1. Before cutting, make certain the cutting arm and table area are at their correct settings and firmly locked in
place.
2. Before cutting, determine that the workpiece is the right size for the saw.
3. Place the workpiece on the table and hold or clamp it firmly against the fence.
4. WARNING: If the workpiece causes your hand to be inside the table hazard area (see section “TABLE
HAZARD AREA”), clamp the workpiece in place before making the cut.
5. For best results, cut at a slow, even cutting rate.
6. Never attempt any freehand cutting (wood that is not held firmly against the fence and table).
AUXILIARY WOOD FENCE
When performing multiple or repetitive cut-off operations
that result in small cut-off pieces (one inch or less), the saw
blade can catch the cut-off pieces and project them out of
the machine or into the blade guard and housing, possibly
causing damage and/or injury. In order to limit the
possibility of personal injury or blade guard damage, an
auxiliary wood fence can be mounted to your saw as
follows:
Holes are provided in the fence to attach an auxiliary fence
(A) and (B) Fig. 31. This auxiliary fence is constructed of
straight wood approximately 1/4” thick by 3/4” high by 16
inches long as shown at (B); and 1/2” thick by 5” high by
17” long (A) Fig. 31.
NOTE: The auxiliary fence (A) is used only with the saw
blade in the 0 degree bevel position (90 degrees) to the
table. The auxiliary fence must be removed for all bevel
cuts (blade tilted).
Fig. 30
A
B
B
A
Fig. 31