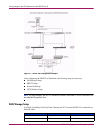
Serving Storage to the iSCSI Initiators from the SR2122 over IP
42 iSCSI SR2122 Storage Router: Getting Started Guide
4. Update /etc/iscsi.conf to include the IP addresses for your iSCSI targets. A sample
configuration file might include entries like this:
DiscoveryAddress=33.33.33.101
The iscsi.conf man page has a more detailed description of the configuration file
format. To read the man page, type:
man iscsi.conf
5. Manually start iSCSI services to test your configuration.
/etc/rc.d/init.d/iscsi start
If there are problems loading the iSCSI kernel module, diagnostic information will be
placed in /var/log/iscsi.log.
The iSCSI initialization will report information on each detected device to the console or
in dmesg(8) output. For example:
Vendor: SEAGATE Model: ST39103FC Rev: 0002
Type: Direct-Access ANSI SCSI revision: 02
Detected scsi disk sda at scsi0, channel 0, id 0, lun 0
SCSI device sda: hdwr sector= 512 bytes.
Sectors= 17783240 [8683 MB] [8.7 GB]
sda: sda1
scsi singledevice 0 0 0 1
Normal disk commands like fdisk, mkfs, and fsck will work on the iSCSI devices like a
local drive.
/proc/scsi/iscsi will contain a file (the controller number) that contains information about
the iSCSI devices.
To manually stop the iSCSI driver enter:
/etc/rc.d/init.d/iscsi stop
6. Modify your init scripts to manage iSCSI. You may also need to change the order of the
boot script to ensure that iSCSI services are started after the network has been initialized.
7. List your iSCSI partitions in /etc/fstab.iscsi. It has the same format as /etc/fstab. The init
scripts will mount and unmount these partitions automatically. See the next few sections
for more details on how to do this correctly.
Device Names
Because Linux assigns SCSI device nodes dynamically whenever a SCSI logical unit is
detected, the mapping from device nodes (e.g /dev/sda, /dev/sdb) to iSCSI targets and logical
units may vary.
Variations in process scheduling and network delay may result in iSCSI targets being mapped
to different SCSI device nodes every time the driver is started. Because of this variability,
configuring applications or operating system utilities to use the standard SCSI device nodes to
access iSCSI devices may result in SCSI commands being sent to the wrong target or logical
unit.
To provide a more reliable namespace, the iSCSI driver will scan the system to determine the
mapping from SCSI device nodes to iSCSI targets, and then create a tree of directories and
symbolic links under /dev/iscsi to make it easier to use a particular iSCSI target's logical units.