— 20 —
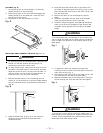
MITERING (Fig. BB)
This sawing operation is the same as crosscutting except
the miter gauge is locked at an angle other than 90
1. Hold the workpiece (2) firmly against the miter
gauge (3).
2. Feed the workpiece slowly into the blade (1) to
prevent the workpiece from moving.
Fig. BB
3
2
1
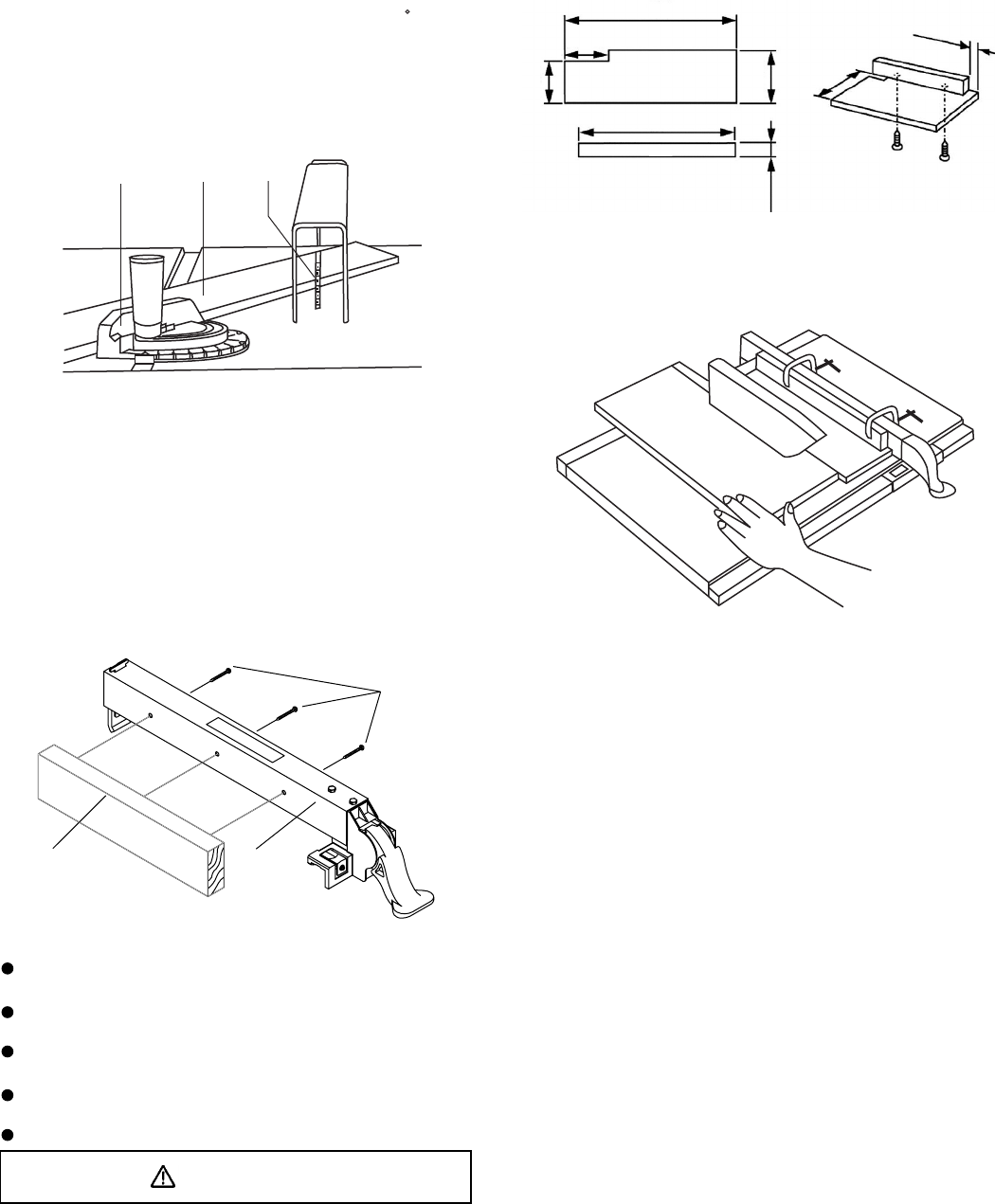
USING WOOD FACING ON THE RIP FENCE (Fig. CC)
When performing some special cutting operations, add a
wood facing (1) to either side of the rip fence (2).
1 . Use a smooth straight 3/4" thick wood board (1) that is
as long as the rip fence.
2. Attach the wood facing to the fence with wood screw
(3) through the hole in the fence. A wood fence should
be used when ripping material such as thin paneling
to prevent the material from catching between the
bottom of the fence and the table.
Fig. CC
1
2
3
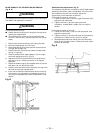
AUXILIARY FENCE (Fig. CC-1)
Making the base:
Start with a piece of 3/8" plywood at least 5-1/2" wide
or wider and 30" long or longer.
Cut the piece to shape and size shown:
Making the side:
Start with a piece of 3/4" plywood at least 2-3/8" wide
or wider and 27" long or longer.
Cut the piece to shape and size shown:
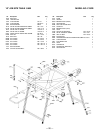
Putting it together:
Put the pieces together, as shown:
WARNING
Make sure the screw heads do not stick out from the
bottom of the base, they must be flush or recessed.
The bottom must be flat and smooth enough to rest on
the saw table without rocking.
Fig. CC-1
30"
27"
2-5/8"
3/4" Thick plywood side
3/4" Thick plywood base
3-1/2"
5-1/2"
2-3/8"
4-3/4
"
1-1/4
"
Attach auxiliary fence to rip fence with two "C" clamps.
(Fig. CC-2)
Fig. CC-2