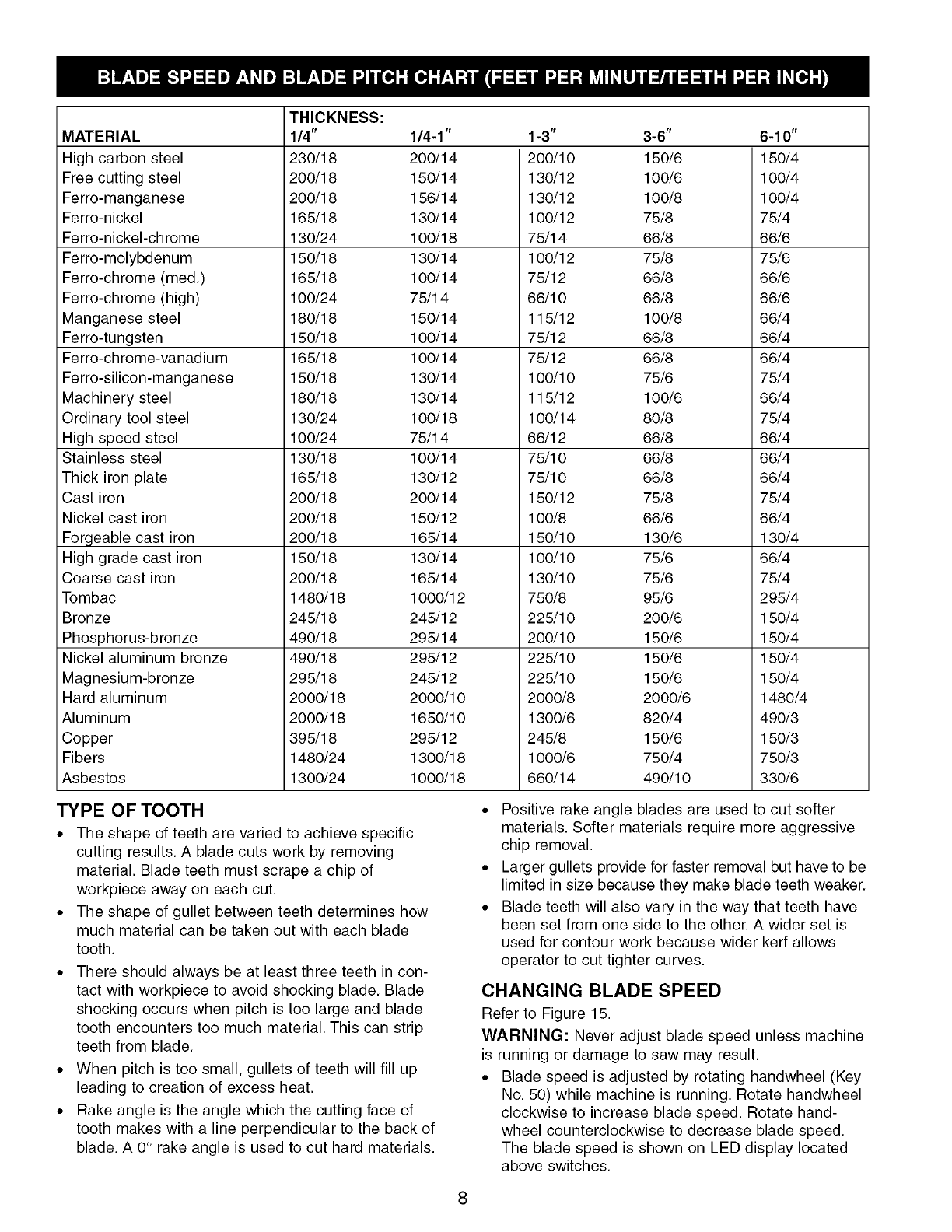
MATERIAL
Highcarbonsteel
Freecuttingsteel
Ferro-manganese
Ferro-nickel
Ferro-nickel-chrome
Ferro-molybdenum
Ferro-chrome(med.)
Ferro-chrome(high)
Manganesesteel
Ferro-tungsten
Ferro-chrome-vanadium
Ferro-silicon-manganese
Machinerysteel
Ordinarytoolsteel
Highspeedsteel
Stainlesssteel
Thickironplate
Castiron
Nickelcastiron
Forgeablecastiron
Highgradecastiron
Coarsecastiron
Tombac
Bronze
Phosphorus-bronze
Nickelaluminumbronze
THICKNESS:
1/4"
230/18
200/18
200/18
165/18
130/24
150/18
165/18
100/24
180/18
150/18
165/18
150/18
180/18
130/24
100/24
130/18
165/18
200/18
200/18
200/18
150/18
200/18
1480/18
245/18
490/18
490/18
1/4-1"
200/14
150/14
156/14
130/14
100/18
130/14
100/14
75/14
150/14
100/14
100/14
130/14
130/14
100/18
75/14
100/14
130/12
200/14
150/12
165/14
130/14
165/14
1000/12
245/12
295/14
295/12
.3 tt
200/10
130/12
130/12
100/12
75/14
100/12
75/12
66/10
115/12
75/12
75/12
100/10
115/12
100/14
66/12
75/10
75/10
150/12
100/8
150/10
100/10
130/10
750/8
225/10
200/10
225/10
.6 tr
150/6
100/6
100/8
75/8
66/8
75/8
66/8
66/8
100/8
66/8
66/8
75/6
100/6
80/8
66/8
66/8
66/8
75/8
66/6
130/6
75/6
75/6
95/6
200/6
150/6
150/6
Magnesium-bronze
Hard aluminum
Aluminum
Copper
Fibers
Asbestos
295/18
2000/18
2000/18
395/18
1480/24
1300/24
245/12
2000/10
1650/10
295/12
1300/18
1000/18
225/10
2000/8
1300/6
245/8
1000/6
660/14
150/6
2000/6
820/4
150/6
750/4
490/10
6-1O"
150/4
100/4
100/4
75/4
66/6
75/6
66/6
66/6
66/4
66/4
66/4
75/4
66/4
75/4
66/4
66/4
66/4
75/4
66/4
130/4
66/4
75/4
295/4
150/4
150/4
150/4
150/4
1480/4
490/3
150/3
750/3
330/6
TYPE OF TOOTH
• The shape of teeth are varied to achieve specific
cutting results. A blade cuts work by removing
material. Blade teeth must scrape a chip of
workpiece away on each cut.
• The shape of gullet between teeth determines how
much material can be taken out with each blade
tooth.
• There should always be at least three teeth in con-
tact with workpiece to avoid shocking blade. Blade
shocking occurs when pitch is too large and blade
tooth encounters too much material. This can strip
teeth from blade.
• When pitch is too small, gullets of teeth will fill up
leading to creation of excess heat.
• Rake angle is the angle which the cutting face of
tooth makes with a line perpendicular to the back of
blade. A 0° rake angle is used to cut hard materials.
• Positive rake angle blades are used to cut softer
materials. Softer materials require more aggressive
chip removal.
• Larger gullets provide for faster removal but have to be
limited in size because they make blade teeth weaker.
• Blade teeth will also vary in the way that teeth have
been set from one side to the other. A wider set is
used for contour work because wider kerf allows
operator to cut tighter curves.
CHANGING BLADE SPEED
Refer to Figure 15.
WARNING: Never adjust blade speed unless machine
is running or damage to saw may result.
• Blade speed is adjusted by rotating handwheel (Key
No. 50) while machine is running. Rotate handwheel
clockwise to increase blade speed. Rotate hand-
wheel counterclockwise to decrease blade speed.
The blade speed is shown on LED display located
above switches.
8