5.7 Standard Comparison Functions
179
FXCPU Structured Programming Manual
(Application Functions)
1
Outline
2
Function List
3
Function
Construction
4
How to Read
Explanation of
Functions
5
Applied
Functions
6
Standard
Function Blocks
A
Correspondence
between Devices
and Addresses
5.7.6 NE_E
Outline
This function compares data with regard to "≠ (unequal)".
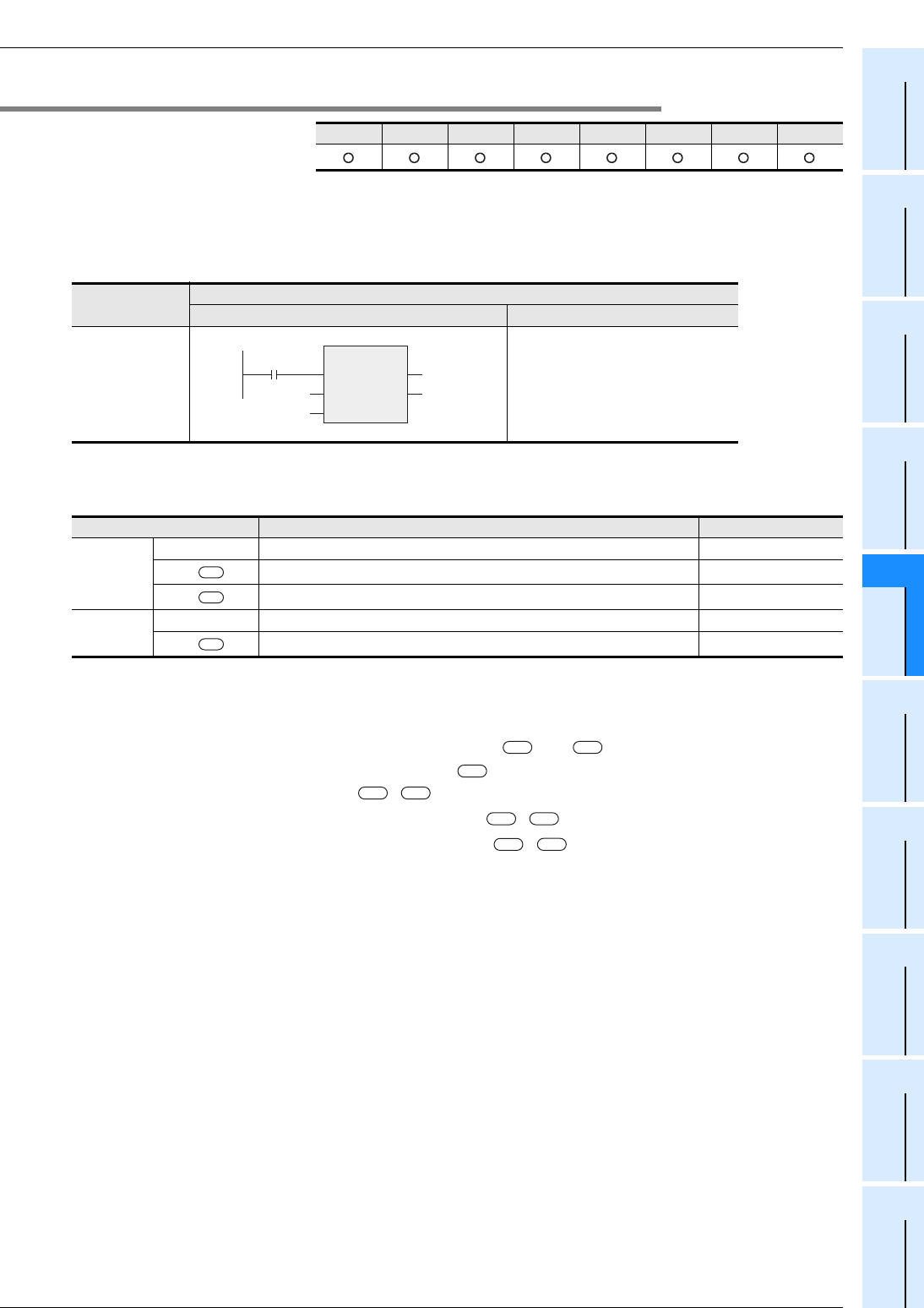
1. Format
*1. Output variable
2. Set data
In explanation of functions, I/O variables inside ( ) are described.
Explanation of function and operation
This function compares the contents of devices specified in and , and outputs the operation result
expressed as the bit type data to a device specified in .
This function executes comparison [ ≠ ].
a) This function outputs "TRUE" when in the case of " ≠ "
b) This function outputs "FALSE" when in the case of " = "
Cautions
When handling 32-bit data in structured programs, you cannot specify 16-bit devices directly, different from
simple projects. Use labels when handling 32-bit data.
You can specify 32-bit counters directly, however, because they are 32-bit devices. Use global labels when
specifying labels.
FX3U(C) FX3G FX2N(C) FX1N(C) FX1S
FX
U
/FX
2C
FX0N FX0(S)
Function name
Expression in each language
Structured ladder ST
NE_E
NE_E(EN,_IN1,_IN2,Output label);
Example:
NE_E(X000,D0,D10,M0);
Variable Description Data type
Input
variable
EN Execution condition Bit
_IN1 ( )
Compared data, or word device which stores such data ANY_SIMPLE
_IN2 ( )
Compared data, or word device which stores such data ANY_SIMPLE
Output
variable
ENO Execution status Bit
*1 ( )
Device which will store the comparison result Bit
NE_E
EN ENO
*1
M0
X000
_IN1D0
_IN2D10
s1
s2
d
s1
s2
d
s1
s2
s1
s2
s1
s2


















