TRG-TRC004-EN 5
period one
Compressor Types
notes
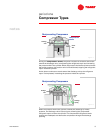
During the compression stroke, the piston reverses its direction and travels
toward the discharge valve, compressing the refrigerant vapor and increasing
the pressure within the cylinder. When the pressure inside the cylinder exceeds
the suction pressure, the suction valve is forced closed, trapping the refrigerant
vapor inside the cylinder.
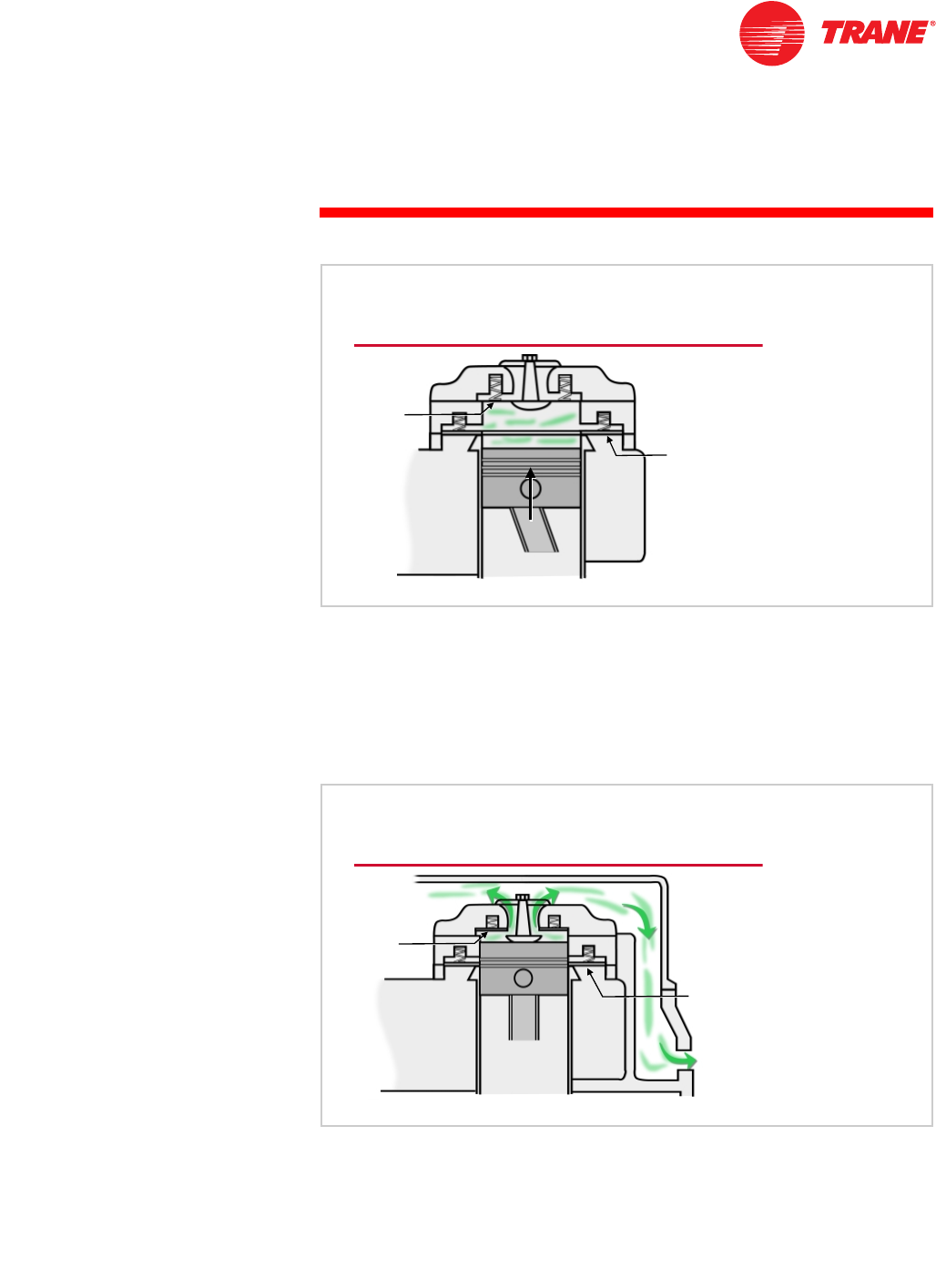
As the piston continues to travel toward the discharge valve, the refrigerant
vapor is compressed, increasing the pressure inside the cylinder.
When the pressure within the cylinder exceeds the discharge (or head)
pressure, the discharge valve is forced open, allowing the compressed
refrigerant vapor to leave the cylinder. The compressed refrigerant travels
through the headspace and leaves the compressor through the discharge
opening.
5HFLSURFDWLQJ&RPSUHVVRU
VXFWLRQ
VXFWLRQ
YDOYH
YDOYH
GLVFKDUJH
GLVFKDUJH
YDOYH
YDOYH
FRPSUHVVLRQ
VWURNH
Figure 7
5HFLSURFDWLQJ&RPSUHVVRU
GLVFKDUJH
GLVFKDUJH
YDOYH
YDOYH
VXFWLRQ
VXFWLRQ
YDOYH
YDOYH
GLVFKDUJH
GLVFKDUJH
RSHQLQJ
RSHQLQJ
KHDGVSDFH
KHDGVSDFH
Figure 8