TRG-TRC004-EN 11
period one
Compressor Types
notes
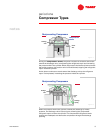
The rotors are meshed and fit, with very close tolerances, within the
compressor housing. The gap between the two rotors is sealed with oil,
preventing the compressed refrigerant vapor from escaping through the mating
surfaces.
Only the male rotor is driven by the compressor motor. The lobes of the male
rotor engage and drive the female rotor, causing the two parts to counter-
rotate.
Refrigerant vapor enters the compressor housing through the intake port and
fills the pockets formed by the lobes of the rotors. As the rotors turn, they push
these pockets of refrigerant toward the discharge end of the compressor.
After the pockets of refrigerant travel past the intake port area, the vapor, still at
suction pressure, is confined within the pockets by the compressor housing.
+HOLFDO5RWDU\&RPSUHVVRU
PDOHURWRU
PDOHURWRU
IHPDOHURWRU
IHPDOHURWRU
KRXVLQJ
KRXVLQJ
Figure 16
+HOLFDO5RWDU\&RPSUHVVRU
LQWDNH
LQWDNH
SRUW
SRUW
SRFNHWRIUHIULJHUDQWYDSRU
SRFNHWRIUHIULJHUDQWYDSRU
Figure 17