34 TRG-TRC004-EN
notes
period three
The Compressor in a System
suction temperature for a specific application depends on the system operating
conditions and the evaporator design.)
Evaporator freeze protection in a chilled-water application is accomplished by
sensing the temperature of the water in the evaporator. If the water approaches
32°F [0°C], the compressor is shut off to protect the evaporator from freezing.
Most chilled water-equipment includes this protection as part of the controls for
the equipment.
In a direct-expansion (DX) application, where the refrigerant in the evaporator is
cooling air, frost protection can be accomplished in a number of ways. As
mentioned, if the surface temperature of the coil gets too cold, the moisture
that condenses out of the air can form frost on the surface of the coil. This “coil
frosting” is detrimental to system performance and compressor reliability.
Historically, in DX air-conditioning applications, hot gas bypass, coil pressure
regulators, and defrost cycles initiated by a timer, pressure sensor, or
temperature sensor are a few of the methods that have been used to prevent
evaporator frosting. This clinic will focus on two of these—a defrost cycle
initiated by a temperature sensor and hot gas bypass.
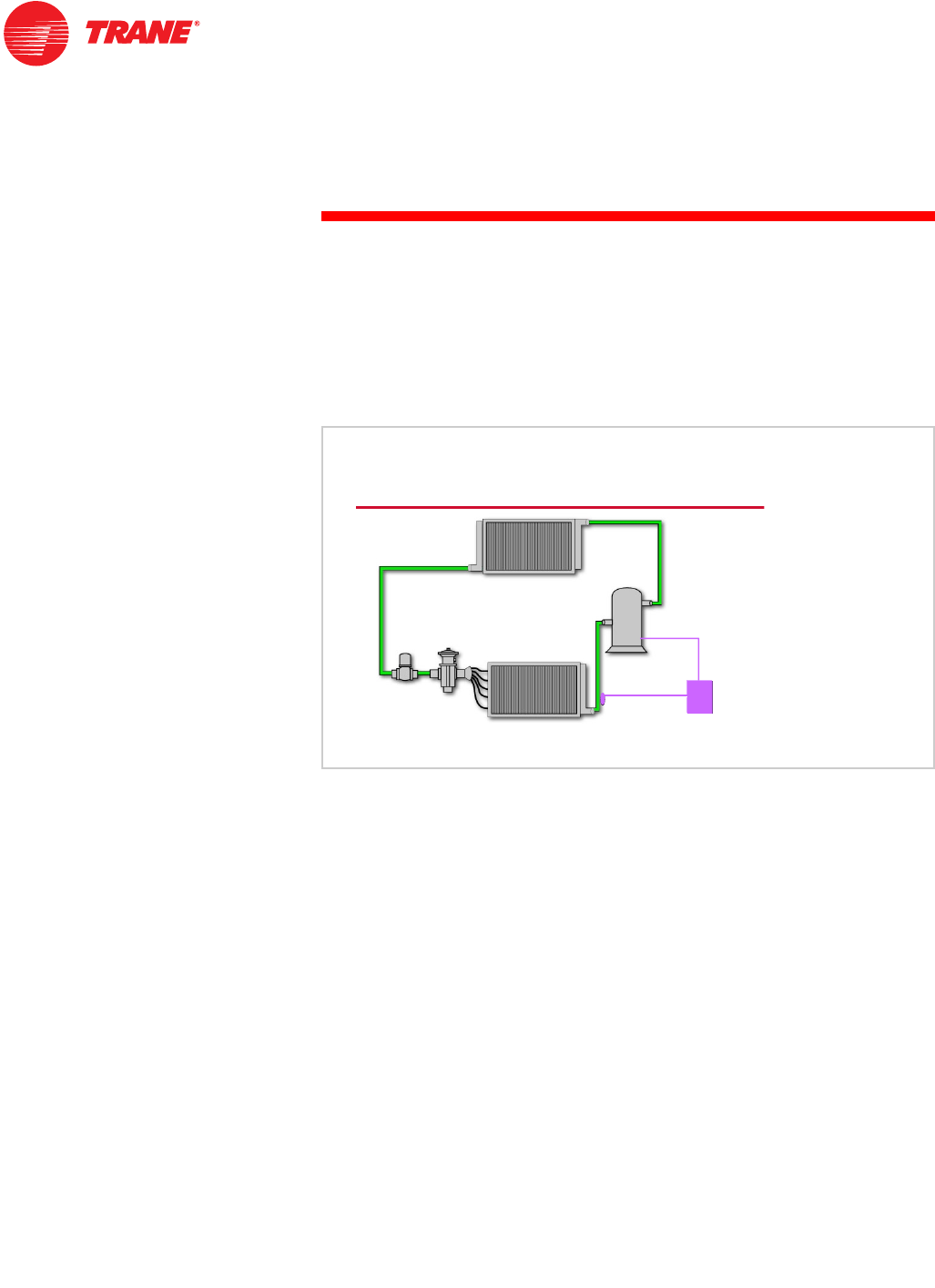
A temperature sensor on the suction line leaving the evaporator is used to
determine if the coil reaches a frosting condition. Compressors are turned off
and the supply fan continues to run to de-ice the coil. Timers prevent the
compressors from rapid cycling.
This control scheme (referred to by Trane as FROSTAT™) is especially well
suited for equipment using scroll compressors, which are designed to start and
stop much more often than large reciprocating compressors.
6HQVLQJ6XFWLRQ7HPSHUDWXUH
H[SDQVLRQ
H[SDQVLRQ
YDOYH
YDOYH
HYDSRUDWRU
HYDSRUDWRU
FRQGHQVHU
FRQGHQVHU
FRPSUHVVRU
FRPSUHVVRU
VXFWLRQ
VXFWLRQ
OLQH
OLQH
VHQVRU
VHQVRU
Figure 48


















