Configuring Subscriber-End Broadband Access Router Features
Voice over IP Operations
MC-617
Cisco IOS Multiservice Applications Configuration Guide
Port address translation (PAT) is a similar mechanism that enables all internal hosts to share a single
registered IP address (many-to-one translation). When combined, NAT/PAT has the following
capabilities:
• Allows customers to maintain their own private networks while giving them full Internet access
through the use of one or more global IP addresses
• Allows several private IP addresses to use the same global IP address by using address overloading
• Facilitates configuration and permits a large network of users to reach the network by using one
Cisco uBR900 series cable access router and the same DOCSIS cable interface IP address
• Eliminates the need to readdress all hosts with existing private network addresses (one-to-one
translation) or by enabling all internal hosts to share a single registered IP address (many-to-one
translation, also known as PAT)
• Enables packets to be routed correctly to and from the outside world by using the Cisco uBR900
series cable access router
• Allows personal computers on the Ethernet interface to have IP addresses to be mapped to the cable
interface IP address
Routing protocols will run on the Ethernet interface instead of the cable interface, and all packets
received are translated to the correct private network IP address and routed out the Ethernet interface.
This eliminates the need to run RIP on the cable interface.
To implement NAT on the Cisco uBR900 series, the Ethernet interface is configured with an “inside”
address and the cable interface is configured with an “outside” address. The Cisco uBR900 series also
supports configuration of static connections, dynamic connections, and address pools.
Voice over IP Operations
Note Voice features are available only on the Cisco uBR924 cable access router.
The Cisco uBR924 cable access router uses packets to transmit and receive digitized voice over an IP
network. Voice signals are packetized and transported in compliance with H.323 or SGCP. H.323 is an
International Telecommunications Union (ITU) standard that specifies call signalling and control
protocols for a shared IP data network. SGCP is an alternative to the H.323 protocol that provides
signalling and feature negotiation using a remote call agent (CA).
SGCP eliminates the need for a dial plan mapper. It also eliminates the need for static configuration on
the router to map IP addresses to telephone numbers because this function is provided by the remote CA.
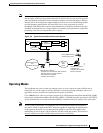
Figure 113 illustrates a broadband cable system that supports VoIP transmission. QoS and prioritization
schemes are used to enable real-time (voice) and nonreal-time traffic to coexist on the same channel. The
CMTS routes IP telephony calls intermixed with other data traffic.