5-3-3
DC
OUTPUT
-
DC output
is
taken out
from
the DC coil and is fed to
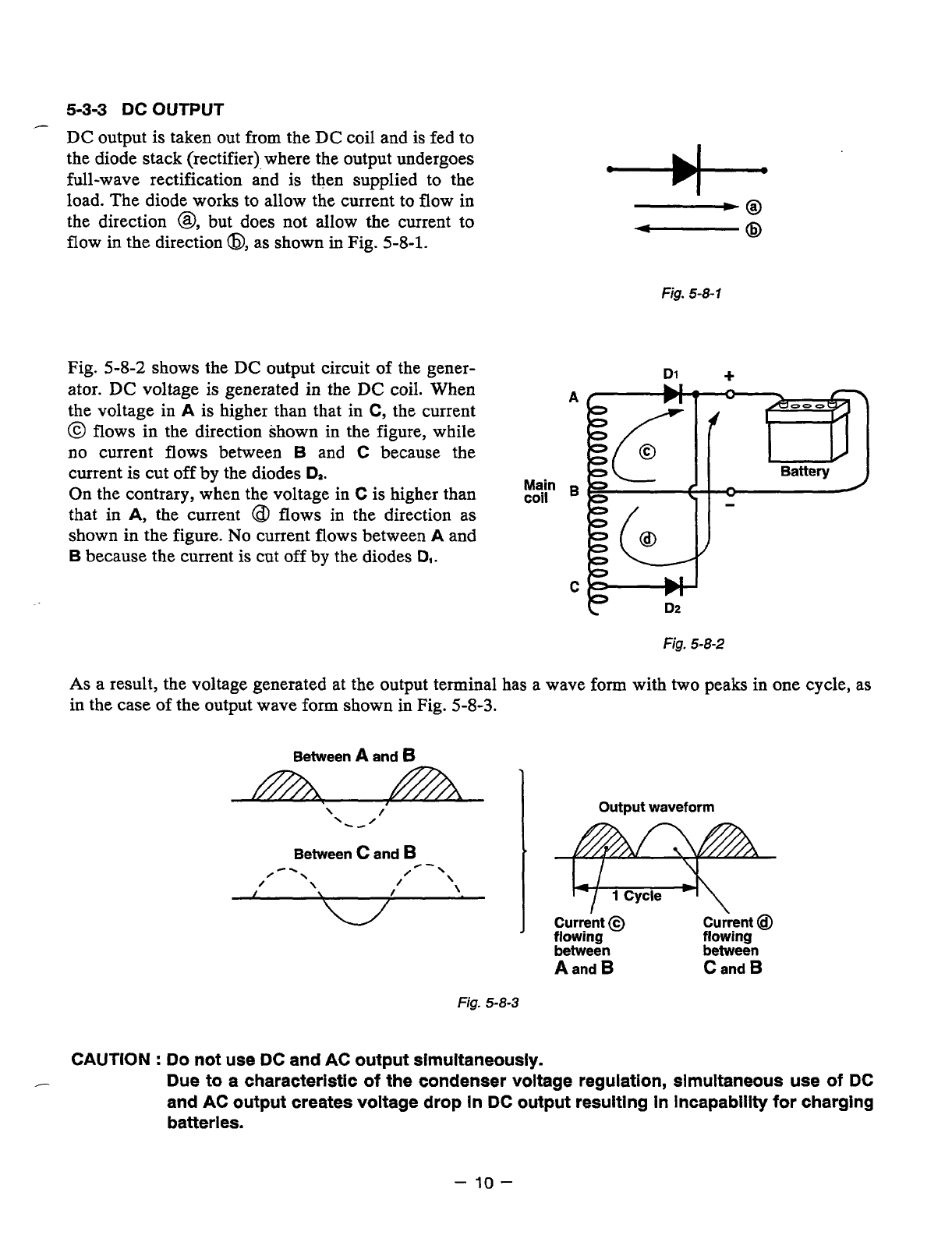
the diode stack (rectifier) where the output undergoes
full-wave rectification and is then supplied to the
load. The diode works to allow the current to
flow
in
the direction
@,
but does not allow the current to
flow in the direction
8,
as shown
in
Fig.
5-8-1.
Fig.
5-8-2
shows the DC output circuit
of
the gener-
ator.
DC
voltage
is
generated in the
DC
coil. When
the voltage in
A
is higher than that
in
Cy
the current
@
flows in the direction shown in the figure, while
no current flows between
B
and
C
because the
current
is
cut off by the diodes
D,.
On
the
contrary, when the voltage in
C
is higher than
that in
A,
the current
@
flows in the direction as
shown in the figure.
No
current flows between
A
and
B
because the current is cut off by the diodes
D,.
Main
coil
4
-a
-0
Fig.
5-8-1
Dl
+
Fig.
5-8-2
As
a result, the voltage generated at the output terminal has a wave form with two peaks in one cycle, as
in the case of the output wave form shown in Fig.
5-8-3.
Between
A
and
6
\
/
1
'"0
Between
c
and
B
-.
0\
/-
/
\
/
'\
I
\
I
\
Fig.
5-8-3
Output
waveform
j
Curre'nt
0
flowing flowing
between between
A
and
B
C
and
B
CAUTION
:
Do not use DC and
AC
output simultaneously.
-
Due to a characteristic
of
the condenser voltage regulation, simultaneous use of DC
and
AC
output creates voltage drop In
DC
output resulting in incapability for charging
batterles.
-
10
-
