Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
30
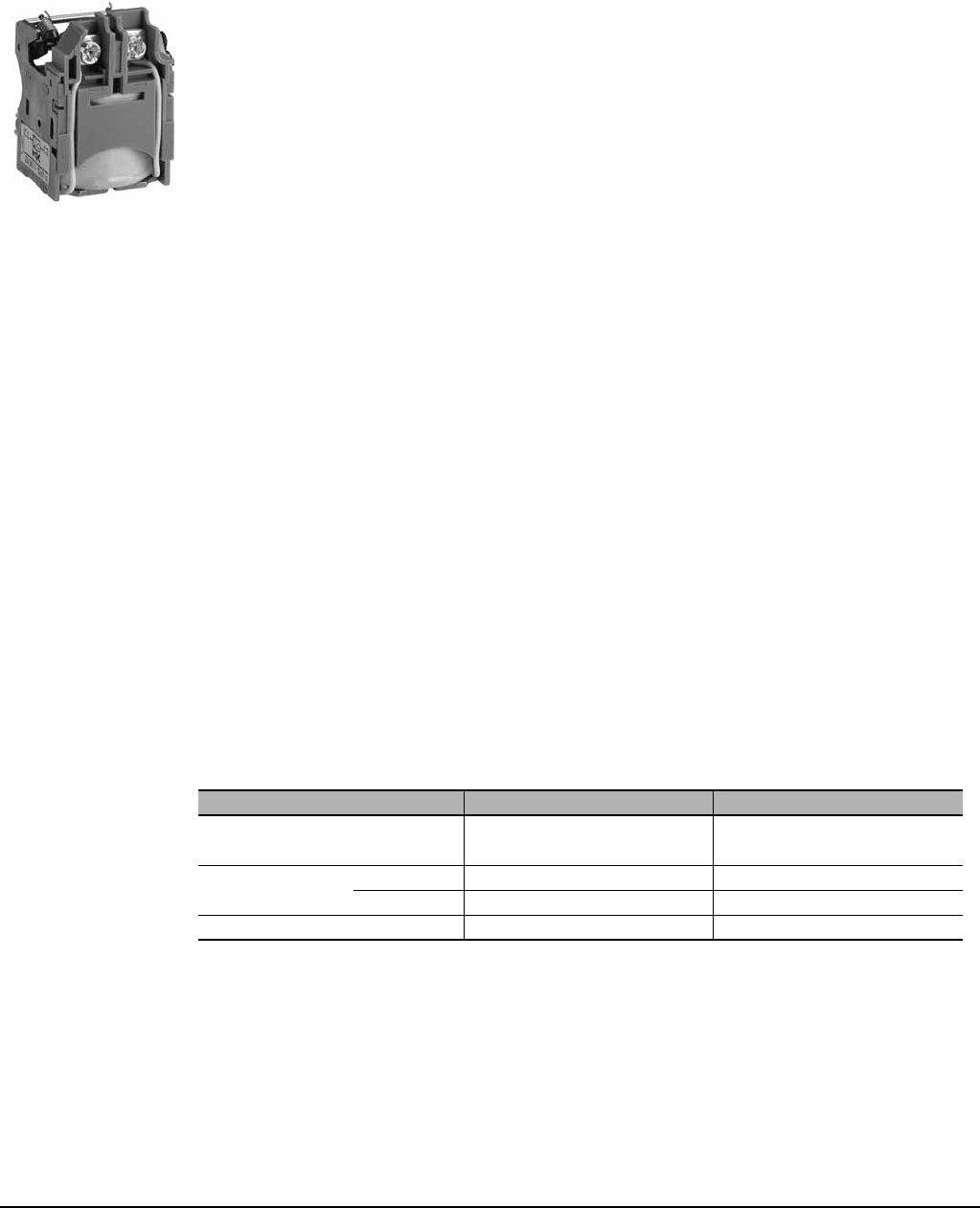
SHUNT TRIP AND UNDERVOLTAGE TRIP
A voltage release can be used to trip the circuit breaker via a control signal.
Undervoltage trip
(MN)
• Trips circuit breaker when the control voltage drops below a tripping threshold
• Drops out between 35% and 70% of rated voltage
• Circuit breaker closing is possible only if the voltage exceeds 85% of rated voltage
• Permanent type
• If an overvoltage condition exists, operation of circuit breaker closing mechanism will not permit the
main contacts to touch, even momentarily
Shunt trip (MX) • Trips the circuit breaker when control voltage rises above 70% of its rated voltage
• Impulse type ≥ 20 ms or maintained control signals
• AC shunt trips can be operated at 55% of their rated voltage, making them suitable for ground-fault
protection when combined with a Class I ground-fault sensing element
Operation • The circuit breaker must be reset locally after being tripped by shunt trip or undervoltage trip
(MN or MX)
• MN or MX tripping has priority over manual (or motor operator) closing; in the presence of a
standing trip order such an action does not result in any closing, even temporarily, of the main
contacts
• Endurance: 50% of the rated mechanical endurance of the circuit breaker for Compact
®
NSF150–
NSJ600 circuit breakers
Installation and
Connection
• Accessories are common to NSF and NSJ circuit breakers and are located within the circuit breaker
behind front accessory cover
• Each terminal may be connected by one #18–#14 AWG (1.0–2.5 mm
2
) stranded copper wire
06153102
Electrical Characteristics
AC DC
Rated Voltage (V)
24, 48, 110–130, 208–277, 380–480, 525, 600 12, 24, 30, 48, 60, 125, 250
Consumption
Pickup (MX) < 10 VA < 5 W
Seal-in (MN) < 5 VA < 5 W
Clearing Time (ms)
< 50 < 50