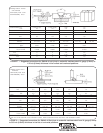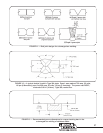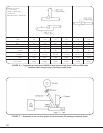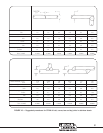
35
SOURCES OF
ADDITIONAL
INFORMATION
Additional information on the welding
of stainless steels can be obtained
from the sources listed below:
The Welding Handbook
7th Edition, Volume 4, Chapter 2 –
American Welding Society
ANSI/AWS D10.4
Recommended Practices for
Welding Austenitic Stainless Steel
Piping and Tubing – American
Welding Society
AWS – A4.2
Standard Procedures for
Calibrating Magnetic Instruments
to Measure the Delta Ferrite
Content of Austenitic and Duplex
Ferritic-Austenitic Stainless Steel
Weld Metal – American Welding
Society
AWS – A5.4
Specification for Stainless Steel
Electrodes for Shielded Metal Arc
Welding – American Welding
Society
AWS – A5.9
Specification for Bare Stainless
Steel Welding Electrodes and
Rods – American Welding Society
AWS – A5.22
Specification Stainless Steel
Electrodes for Flux-Cored Arc
Welding and Stainless Steel Cored
Rods for Gas Tungsten Arc
Welding – American Welding
Society
AWS – A5.30
Specification for Consumable
Inserts – American Welding
Society
ASM Metals Handbook
Volume 6 – Welding and Brazing –
8th Edition – ASM International
ASM Metals Handbook
Volume 6 – Welding, Brazing and
Soldering – 9th Edition – ASM
International
AWS – FMC
Filler Metal Comparison Charts –
American Welding Society
Literature from filler metal
manufacturers:
ASM Metals Handbook
Volume 1 – Properties and
Selection of Metals, 8th Edition –
ASM International
ASM Metals Handbook
Volume 3 – Properties and
Selection of Stainless Steels, Tool
Materials and Special Purpose
Metals, 9th Edition – ASM
International
The Making, Shaping and Treating
of Steel
10th Edition, United States Steel
Corporation
ANSI – Z49.1
Safety in Welding, Cutting and
Allied Processes – American
Welding Society
Welding Metallurgy of Stainless
Steels
by Erich Folkhard, Springer -
Verlag, New York
WARNING –
HEALTH & SAFETY
NOTICE
Protect yourself and others. Read
and understand the label provided
with filler material for welding.
FUMES AND GASES can be
dangerous to your health. ARC RAYS
can injure eyes and burn skin.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Read and understand the
manufacturer’s instructions and
your employer’s safety practices.
• Keep your head out of the fumes.
• Use enough ventilation, exhaust at
the arc, or both, to keep fumes
and gases away from your
breathing zone and the general
area.
• Wear correct eye, ear and body
protection.
• Do not touch live electrical parts
or permit electrically live parts or
electrodes to contact skin or your
clothing or gloves if they are wet.
• Insulate yourself from work and
ground.
IMPORTANT:
Special ventilation and/or exhaust
are required when welding high
chromium alloys such as stainless
steels.
Fumes from the normal use of
stainless steel filler materials contain
significant quantities of chromium
compounds. The (TLV) Threshold
Limit Value for chromium (0.5 mg/m
3
)
and/or chromium VI (0.05 mg/m
3
)
will be exceeded before reaching the
5.0 mg/m
3
maximum exposure
guideline for total welding fume.
BEFORE USING, READ AND
UNDERSTAND THE MATERIAL
SAFETY DATA SHEET (MSDS)* FOR
THE FILLER MATERIAL TO BE
USED.
• See American National Standard
Z49.1, Safety in Welding, Cutting
and Allied Processes, published
by the American Welding Society,
550 N.W. LeJeune Road, Miami,
Florida 33126;
OSHA Safety and Health
Standards, 29 CFR 1910,
available from the U.S.
Government Printing Office,
Washington, DC 20402-0001
* Available from
The Lincoln Electric Company
(for Lincoln products)
22801 St. Clair Avenue
Cleveland, Ohio 44117