Configuration How-to’s
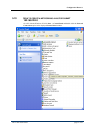
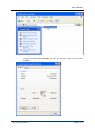
For example, to give local users whose extension numbers start with 56 the capability to
make outgoing calls through dialing technical prefix 0, configure source and destination
number transformation as shown in the table below:
Match Pattern Result
Source ^56.* ^(56.*) $1
Destination ^0.* ^0(.*) $1
According to this rule prefix 0 will be cut off from the destination number because the
internal prefix used in the system is of no relevance to the gateway sending calls outside the
system.
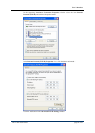
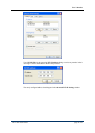
The syntax of regular expressions appearing in the field
is identical to that of
regular expressions entered in the field
.
The table below contains a list of regular expression constructs applicable in configuring the
system.
Table 5 Summary of regular expression constructs
Construct Matches
Characters
x The character x
\0n The character with octal value 0n (0 <= n <= 7)
\0nn The character with octal value 0nn (0 <= n <= 7)
\0mnn The character with octal value 0mnn (0 <= m <= 3,
0 <= n <= 7)
\xhh The character with hexadecimal value 0xhh
\uhhhh The character with hexadecimal value 0xhhhh
\t
The tab character ('\u0009')
\n
The newline (line feed) character ('\u000A')
Character classes
[abc]
a, b, or c (simple class)
[^abc]
Any character except a, b, or c (negation)
[a-zA-Z]
a through z or A through Z, inclusive (range)
[a-d[m-p]]
a through d, or m through p: [a-dm-p] (union)
[a-z&&[def]]
d, e, or f (intersection)
[a-z&&[^bc]]
a through z, except for b and c: [ad-z] (subtraction)
[a-z&&[^m-p]]
a through z, and not m through p: [a-lq-z](subtraction)
Predefined character classes
DVX-7090 VoIP Router page 64 of 83