-34-
G0636X 17" Ultimate Bandsaw
One of the benefits of a bandsaw is its ability to cut
multiple copies of a particular shape by stacking
a number of workpieces together. Before making
stacked cuts, ensure that both the table and the
blade are properly adjusted to 90° (see Page 17).
Otherwise, any error will be compounded.
To complete a stacked cut:
1. Align your pieces from top to bottom to
ensure that each piece has adequate scrap
to provide a clean, unhampered cut.
2. Secure all the pieces together in a manner
that will not interfere with the cutting. Hot
glue on the edges works well, as do brad
nails through the waste portion. (Be careful
not to cut into the brads or you may break the
blade!)
3. On the face of the top piece, lay out the
shape you intend to cut.
4. Make relief cuts perpendicular to the out-
line of your intended shape in areas where
changes in blade direction could strain the
woodgrain or cause the blade kerf to bind.
5. Cut the stack of pieces as though you were
cutting a single piece. Follow your layout line
with the blade kerf on the waste side of your
line, as shown in
Figure 46.
Figure 46. Typical stacked cut.
Selecting the right blade requires a knowledge
of the various blade characteristics to match the
blade with the particular cutting operation.
Blade Length
Measured by the circumference, blade lengths
are usually unique to the brand of your bandsaw
and the distance between wheels. The Model
G0636X is designed for blades that are 160" long.
Refer to Page 37 for blade replacements.
Blade Width
Measured from the back of the blade to the tip of
the blade tooth (the widest point), blade width is
often the first consideration given to blade selec
-
tion. Blade width dictates the largest and smallest
curve that can be cut, as well as how accurately it
can cut a straight line.
The Model G0636X can use blades from
1
⁄8" to
1
3
⁄8" in width. Always pick the size of blade that
best suits your application.
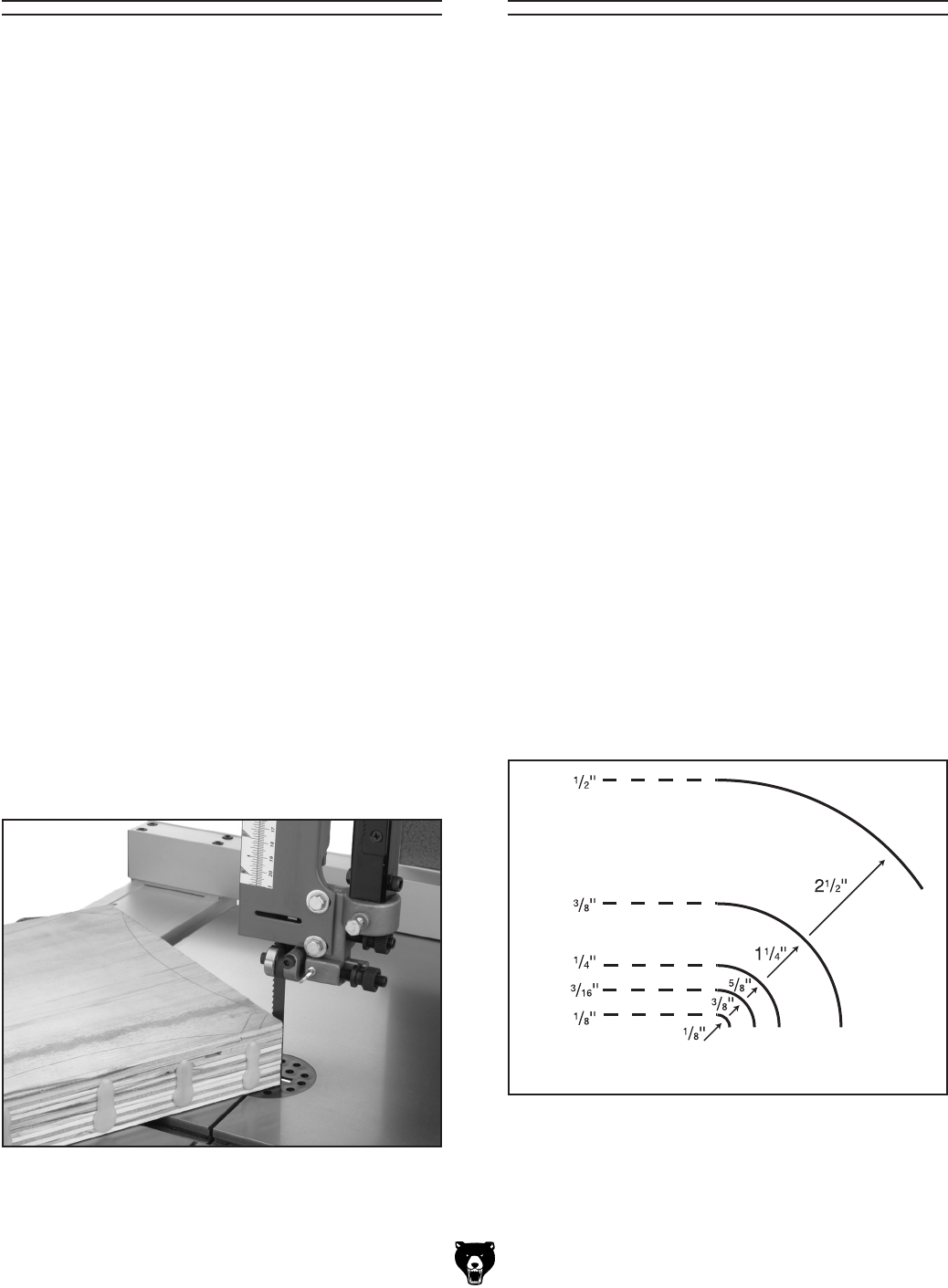
• Curve Cutting: Use the chart in Figure 47 to
determine the correct blade for curve cutting.
Determine the smallest radius curve that will
be cut on your workpiece and use the cor
-
responding blade width.
Figure 47. Blade width radii.
Stacked Cuts Blade Information


















