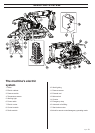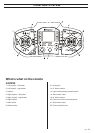
ELECTRIC SYSTEM
General
The electric system consists of a high-voltage circuit
and a low-voltage circuit.
High-voltage circuit
High-voltage is used as a power source for both the
electric motor and the low-voltage circuit. An automat-
ic phase rotation change-over switch ensures that the
electric motor has the correct rotation direction.
Power supply
The power supply from the main must be suffi ciently
powerful and constant to ensure that the electric mo-
tor runs without problems.
Too high or too low voltage causes the electric mo-
tor’s power consumption, and consequently also its
temperature, to increase until the motor’s safety circuit
trips.
Fuses
The fuses in the distribution box protect the electrical
system in conjunction with overloading or breakdown.
The power outlet must be correctly fused with respect
to the electric motor, the length of the power cable
and the area of the power cable’s conductor. The table
“Guide values for mains connection” in the “Techni-
cal data” section shows which fuse is required for the
electric motor.
The machine is equipped with Softstart and can be
started with most types of fuses.
If a fuse keeps blowing there is a fault in the electri-
cal system or in the machine that is connected to it.
Before restarting the machine the source of the fault
must be removed.
Power cable
The machine is connected to the mains with a 3 phase
power cable. It is very important that the cable that is
used is correctly dimensioned, i.e. that it has the cor-
rect cross-sectional area in relation to the length of the
conductor in order to counteract drops in voltage. The
guide values for the cable’s size are set out in the table
’Guide values for main connection” in the ’Technical
data” section.
Low-voltage circuit
The high-voltage current is reduced to low-voltage in
an AC/DC module. It is used to supply power to the
control system and functions such as work lighting
and refi lling pump.
20
- English