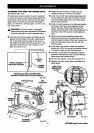
CUTTING AIDS
See Figures 39-41.
Cutting aids are used to improve the setup and help
make the operator's work safer and more accurate.
They can be made from scrap wood and in various
sizes and shapes for specific projects.
The basic types are pushsticks, pushblocks, and
featherboards. If the blade is set 2 in. or more from
the fence, use a pushstick. Use a pushblock when the
blade is between 1/2 in. and 2 in. from the fence. (If
the cut is narrower than 1/2 in., use a different saw.)
Refer to the drawings and instructionsprovided so
you can make safer and more precise cuts.
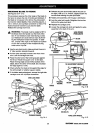
PUSHSTICKS
See Figure 39.
Pushsticks must be narrower than the workpiece, with
a 90" notch in one end and shaped for a grip on the
other end.
PUSHBLOCKS
See Figure 40.
A pushblock has an upright handle with a base
attached to the handle. Some pushblocks have a foot
that extends down from the base and against the
workpiece. The foot is attached to the base with glue
only to prevent damage to the blade.
FEATHERBOARDS
See Figure 4 I.
Featherboards are used for large panels, along with
an auxiliary table and a C-clamp. A featherboard has
an angled end to fit against the edge of the workpiece.
It is clamped in place so the workpiece moves be-
tween either the fence and the featherboard or the
table and featherboard. Slots in the end of the
featherboard help resist kickback and allow for
variations in the width of the workpiece.
_i, WARNING: Clamp the featherboard against the
infeed side of the workpiece. If clamped behind
the blade, it could squeeze the cut edges
together, causing binding and kickback. Kickback
can cause serious injury.
PUSHSTICKS Fig. 39
PUSHBLOCKS Fig. 40
FEATHERBOARD
Fig. 41
Note: The Pushstick designs above are for illustration
: purposes only. They have not been drawn to
scale.
45 I;RRFTSMRIrRADIALSAW315.220380