Modbus Memory Map
489
Communications Guide
http://www.GEindustrial.com/multilin
40
GE Multilin
Memory Map Data
Formats
The data formats used in the Modbus memory map are shown below.
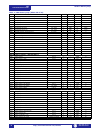
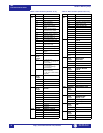
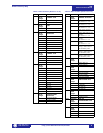
Table 2: Data Formats (Sheet 1 of 12)
CODE TYPE DEFINITION
F1 16 bits UNSIGNED VALUE
Example: 1234 stored as 1234
F2 16 bits UNSIGNED VALUE,
1 DECIMAL PLACE
Example: 123.4 stored as 1234
F3 16 bits UNSIGNED VALUE,
2 DECIMAL PLACES
Example: 12.34 stored as 1234
F4 16 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT
SIGNED VALUE
Example: –1234 stored as –1234 (i.e.
64302)
F5 16 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT
SIGNED VALUE
1 DECIMAL PLACES
Example: -123.4 stored as -1234 (i.e.
64302)
F6 16 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT
SIGNED VALUE
2 DECIMAL PLACES
Example: –12.34 stored as –1234 (i.e.
64302)
F10 32 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT
SIGNED LONG VALUE
1 DECIMAL PLACE
1st 16 bits High Order Word of Long
Value
2nd 16 bits Low Order Word of Long
Value
Example: –12345.6 stored as
–123456 (i.e. 1st word: FFFE hex, 2nd
word: 1DC0 hex)
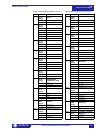
F12 32 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT
SIGNED LONG VALUE
1st 16 bits High Order Word of Long
Value
2nd 16 bits Low Order Word of Long
Value
Example: -123456 stored as -123456
(i.e. 1st word: FFFE hex, 2nd word:
1DC0 hex)
F13 32 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT
SIGNED LONG VALUE,
3 DECIMAL PLACES
1st 16 bits High Order Word of Long
Value
2nd 16 bits Low Order Word of Long
Value
Example: -123.456 stored as -123456
(i.e. 1st word: FFFE hex, 2nd word:
1DC0 hex)
F14 32 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT
SIGNED LONG VALUE,
2 DECIMAL PLACES
1st 16 bits High Order Word of Long
Value
2nd 16 bits Low Order Word of Long
Value
Example: -1234.56 stored as -123456
(i.e. 1st word: FFFE hex, 2nd word:
1DC0 hex)
F15 16 bits HARDWARE REVISION
0000 0000
0000 0001
1 = A
0000 0000
0000 0010
2 = B
... ...
0000 0000
0001 1010
26 = Z
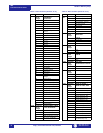
F16 16 bits SOFTWARE REVISION
1111 1111
xxxx xxxx
Major Revision Number
0 to 9 in steps of 1
xxxx xxxx
1111 1111
Minor Revision Number
(two BCD digits)
00 to 99 in steps of 1
Example: Revision 2.30 stored as
0230 hex
F18 32 bits DATE (MM/DD/YYYY)
1st byte Month (1 to 12)
2nd byte Day (1 to 31)
3rd & 4th
byte
Year (1995 to 2094)
Example: Feb. 20, 1996 stored as
34867148 (i.e. 1st word: 0214, 2nd
word 07CC)
F19 32 bits TIME (HH:MM:SS:hh)
1st byte Hours (0 to 23)
2nd byte Minutes (0 to 59)
3rd byte Seconds (0 to 59)
4th byte Hundreds of seconds (0
to 99)
Example: 2:05pm stored as
235208704 (i.e. 1st word: 0E05, 2nd
word 0000)
F20 32 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT
SIGNED LONG VALUE
1st 16 bits High Order Word of Long
Value
2nd 16 bits Low Order Word of Long
Value
Note: -1 means “Never”
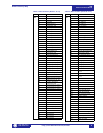
F22 16 bits TWO 8-BIT
CHARACTERS
PACKED INTO 16-BIT
UNSIGNED
MSB First Character
LSB Second Character
Example: String ‘AB’ stored as 4142
hex.
F24 32 bits TIME FORMAT FOR
BROADCAST
1
st
byte Hours (0 to 23)
2
nd
byte Minutes (0 to 59)
3
rd
& 4
th
bytes
Milliseconds (0 to 59999)
Note: Clock resolution
limited to 0.01 sec
Example: 1:15:48:572 stored as
17808828 (i.e., 1
st
word 010F, 2
nd
word BDBC)
Table 2: Data Formats (Sheet 2 of 12)
CODE TYPE DEFINITION