5
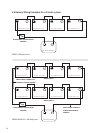
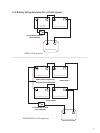
Designthebatteryenclosuretopreventaccumulationandconcentrationofhydrogengasin“pockets”at
the top of the enclosure. Vent the battery compartment from the highest point to the outside. A sloped lid
can also be used to direct the ow of hydrogen to the vent opening.
CAUTION
To reduce risk of injury, charge only deep-cycle lead acid, lead antimony, lead calcium, gel cell or absorbed
glass mat type rechargeable batteries. Other types of batteries may burst, causing personal injury and
damage. Never charge a frozen battery.
SAFETY AND HUMAN FACTORS
Someone should be within range of your voice to come to your aid if needed.•
Keep plenty of fresh water and soap nearby in case battery acid contacts skin, clothing, or eyes.•
Wear complete eye protection. Avoid touching eyes while working near batteries. Wash your hands •
with soap and warm water when done.
If battery acid contacts skin or clothing, wash immediately with soap and water. If acid enters an •
eye,oodtheeyewithcoolrunningwateratonceforatleast15minutesandgetmedicalattention
immediately following.
Baking soda neutralizes lead acid battery electrolyte. Keep a supply on hand in the battery area.•
NEVER smoke or allow a spark or ame in vicinity of a battery or generator.•
Do not contact battery lugs or ring terminals with your skin; this increases the risk of a shock.•
Be extra cautious to reduce the risk of dropping a metal tool onto batteries. It could short-circuit the •
batteries or other electrical parts and can result in re or explosion.
Remove personal metal items such as rings, bracelets, necklaces, and watches when working with a •
battery or other electrical current. A battery can produce a short circuit current high enough to weld
a ring or the like to metal, causing severe burns.
WARNING: WORKING NEAR LEAD ACID BATTERIES CAN BE DANGEROUS. BATTERIES
GENERATE EXPLOSIVE GASES DURING NORMAL OPERATION.
IMPORTANT BATTERY INSTRUCTIONS