CHAPTER
2-1
Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System 8-Slot Line Card Chassis Site Planning Guide
OL-5802-06
2
Power and Cooling
This chapter describes the Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System 8-Slot Line Card Chassis power and
cooling systems. It also provides the power and grounding and cooling requirements for the installation
site to help you plan the site facilities for the system. The Cisco
CRS-1 Carrier Routing System 8-Slot
Line Card Chassis System Description provides detailed information about these components.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Chassis Power System
• General Power and Grounding Requirements
• DC Power Requirements
• AC Power Requirements
• Supplemental Bonding and Grounding
• Chassis Airflow
• Facility Cooling Requirements
Chassis Power System
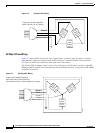
The 8-slot line card chassis can be either DC or AC powered. Each type of power system (DC or AC)
provides power to chassis components. The chassis power system is made up of two input power
distribution units (PDUs) and two power modules, one in each PDU. Each PDU is connected to a
different power source. Input power enters the PDU and is passed to the power module, which provides
7,500 watts of power to the components in the chassis. Each power module has its own circuit breaker.
The Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis uses the AC power PDUs to provide the two types of AC wiring
schemes (Wye and Delta). Each chassis has two PDUs, and each PDU takes one supply which, in the
case of AC, has three internal zones such that two three-zone power supplies provide three redundant
power zones (see the Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System 8-Slot Line Card Chassis System Description
for more information).
Because each PDU is connected to a separate and independent power source, the power system provides
2N power redundancy. During normal operation when both power sources are operational, both sets of
PDUs and power modules function together to power the chassis. However, if a power sources fails, the
other power source provides the other PDU and power module with enough input power to power the
chassis. This 2N power redundancy enables the routing system to operate despite the power failure.
Chassis input power requirements are as follows:
• A DC-powered chassis requires 8,000 watts of DC input power.