Why use XML in databases?
216 PowerDesigner
Why use XML in databases?
XML is becoming a universal data exchange format. An XML file can be
read with any plain text editor. Most of relational databases (RDB) now
support XML so that you can store or retrieve data through XML files.
With an XML model, you can generate an annotated schema that will allow
you to store or retrieve data in a relational database supporting XML. To
generate an annotated schema, you need to attach the appropriate extended
model definition (XEM file) to an XML model mapped (or not) to a PDM.
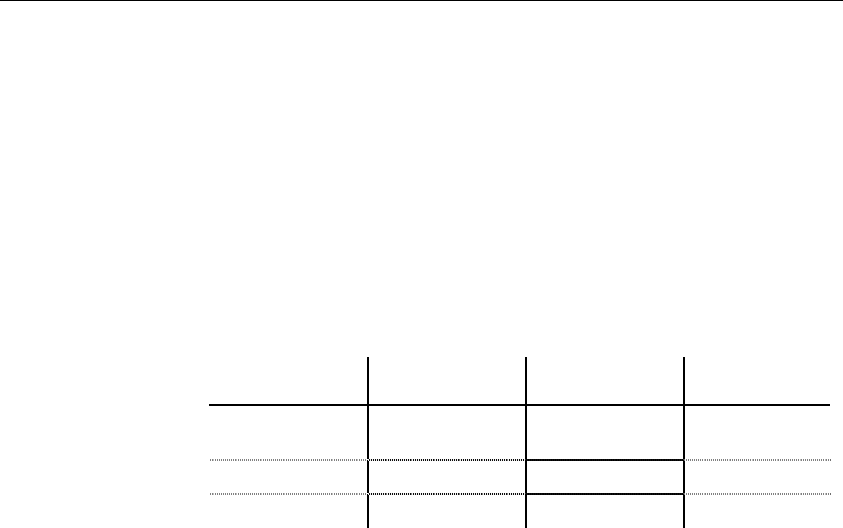
The following table lists the databases supporting XML for which you can
generate annotated schemas:
Database
Mapped XML
model
Targeted XML
language
Required XEM
file
Microsoft SQL
Server 2000
Yes XSD or XDR Microsoft SQL
Server
Oracle 9i2 No XSD Oracle 9i2
IBM DB2 v8.1 Yes DTD IBM DB2 DAD
By attaching the SQL/XML extended model definition to an XML model
mapped to a PDM, you can also generate SQL/XML queries to retrieve data
in an XML format, from relational databases supporting SQL/XML.
The best way to generate SQL/XML queries is to use the XML Builder
Wizard which helps you build an XML model from a PDM. The generated
XML model is mapped to the PDM and automatically linked to the
SQL/XML extended model definition. (See Generating SQL/XML queries)


















